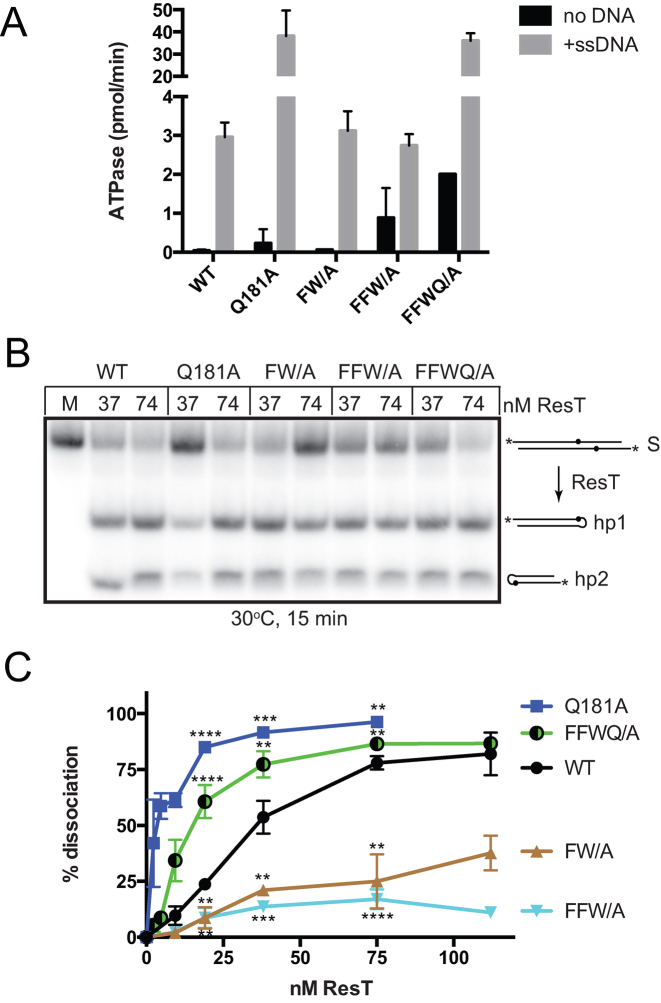
Figure 4.
ResT mutations that differentially affect telomere resolution and DNA unwinding. (A) Summary of ATPase results of the indicated ResT variants, −/+ 10 μg/mL ϕX174 virion. ATPase assays containing 74 nM ResT were incubated at 37°C for 30 min (Q181A) or at 37°C for 120 min for wild type ResT (WT), F93AW94A (FW/A), F92AF93AW94A (FFW/A), or F92AF93AW94AQ181A (FFWQ/A). The mean and standard deviation of at least three independent experiments is shown. (B) 8% PAGE 1× TAE/0.1%SDS gel analysis of telomere resolution assays conducted at 30°C for 15 min. The schematic to the right of the gel indicates the structure of the substrate (S) and of the resulting hp telomere products (hp1 and hp2). The asterisk denotes 5΄-endlabels and the dots the position of the scissile phosphates. (C) % Strand dissociation vs. ResT concentration curves of the indicated ResT variants. The helicase assays were performed by 60 min incubation at 37°C, with 15 nM substrate. Reactions were performed in triplicate and the mean and standard deviation are shown. Differencesbetween each mutant and wild type ResT in reaction conditions containing 37 nM ResT were examined using unpaired t-tests. ** P ≤ 0.01 and *** P ≤ 0.001.