Figure 7.
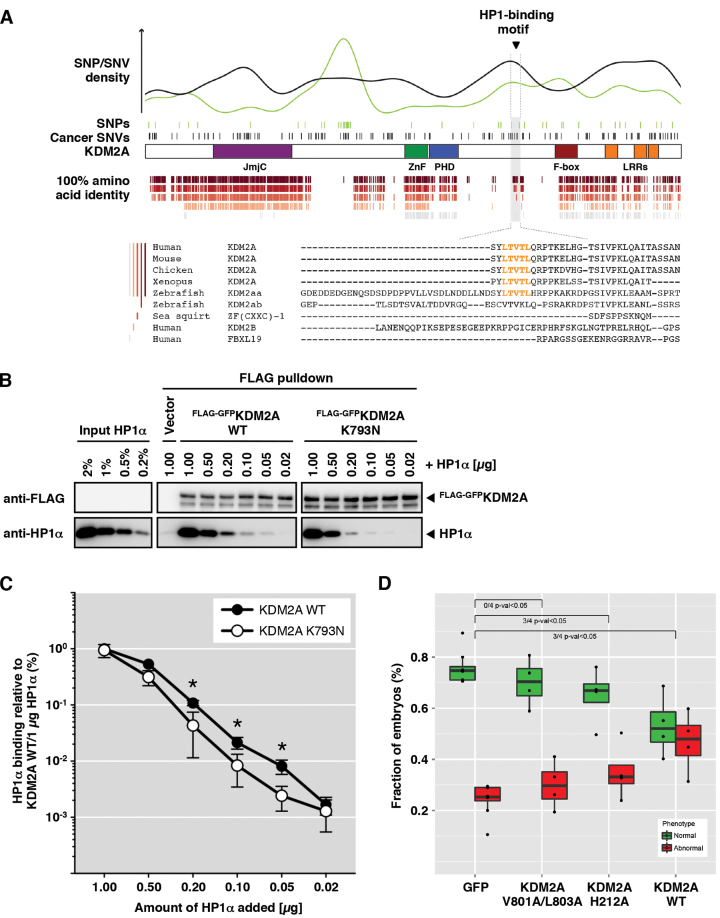
The HP1 interaction is integral to the biological function of KDM2A. (A) Domain-specific patterns of conservation and single nucleotide variations in KDM2A. Missense variants segregating in the human population (SNPs, green ticks) or present in a collection of sequenced tumours (cancer SNVs, black ticks) are indicated in relation to the linear domain architecture of human KDM2A. Correspondingly coloured density plots highlight the anti-correlated incidence of SNPs and cancer SNVs across KDM2A domains (SNP/SNV density). Identical amino acids across different subsets of KDM2A orthologs/gene family members are illustrated below for individual residues (ticks). A Sequence alignment of the region surrounding the HP1 binding motif (LTVTL) demarcated by dotted lines indicates conservation of the motif in KDM2A orthologues but not KDM2B and Fbxl19. A full alignment of KDM2A orthologues spanning the whole protein sequence is provided in Supplementary File 1. (B) The K793N cancer mutation impairs binding of HP1α to KDM2A. FLAG-GFP-tagged KDM2A WT or the K793N cancer mutant were expressed in 293T cells and captured on FLAG-affinity beads. The immobilized KDM2A proteins were then incubated with different amounts of recombinant HP1α as indicated. 40% of the pull-down reactions were resolved by SDS-PAGE and bound proteins detected by immunoblot. Titration of HP1α indicates reduced binding to the K793N mutant compared to KDM2A WT. (C) Quantification of HP1 binding to WT KDM2A and the K793N mutant. The FLAG and HP1α immunoblots shown in Figure 7B were quantified using the chemiluminescence signals associated with the full length FLAG-GFP-KDM2A and HP1α bands. HP1α signals were normalized against the WT KDM2A pull-down with 1 μg HP1α using the FLAG (KDM2A) signals obtained for the individual pull-downs as a relative measure for loading. The figure shows the mean and standard deviation of three independently performed experiments plotted on a logarithmic (log10) scale. Asterisks mark samples in which binding of HP1α to the K793N mutant differs significantly from the WT (P-value < 0.05 by unpaired t-test). The K793N mutant shows ∼50% reduced binding over a wide range of HP1α concentrations. (D) Loss of function of the KDM2A V801A/L803A mutant. Box plot of overexpression phenotypes caused by injecting 3.6 nl of 62.5 ng/μl mRNA of GFP and three human KDM2A constructs into zebrafish embryos shows that there was no significant difference in phenotype between GFP and V801A/L803A mutant KDM2A, whereas in three out of four injections both H212A mutant KDM2A and WT KDM2A showed significantly more abnormal embryos at 24 h.p.f. than the GFP control. Statistical analyses of the individual overexpression experiments can be found in Supplementary Figure S9C–E.