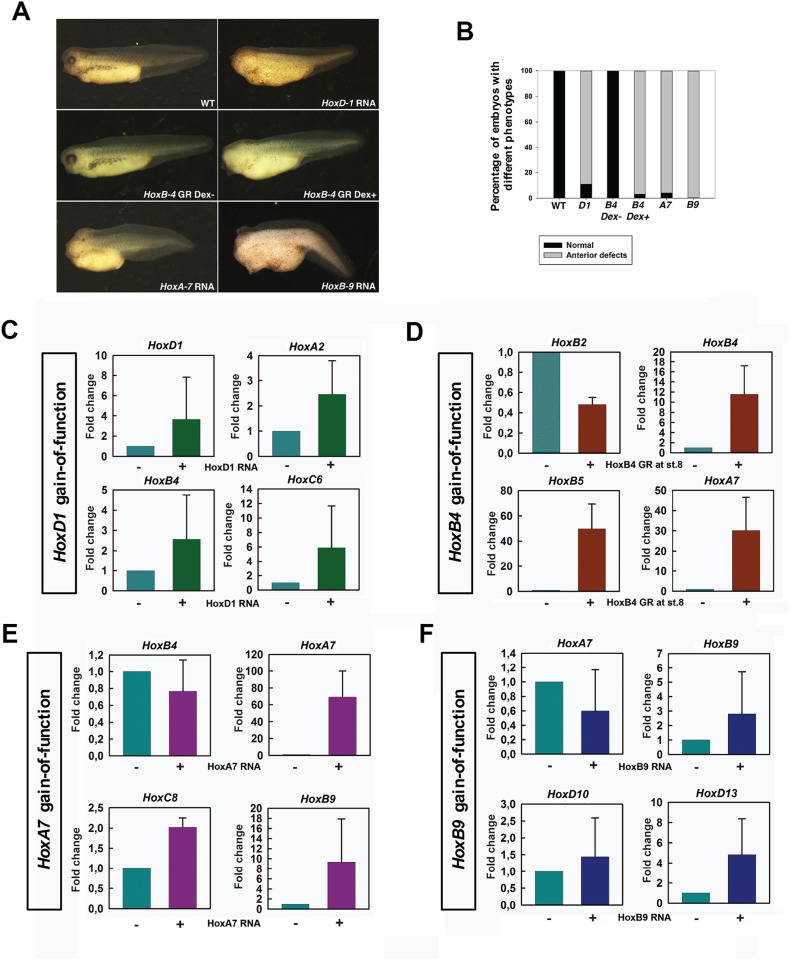
Fig 2. Ectopic Hox expression in wild-type embryos affects axis formation and endogenous Hox expression.
(A) Phenotypes of embryos injected with different Hox RNA. (B) Percentage of embryos showing anterior defects. From left to right: wild-type (n = 30), HoxD-1 injected (n = 54), HoxB-4 GR injected (without Dex treatment) (n = 40), HoxB-4 GR injected (with Dex treatment at st.8) (n = 60), HoxA-7 injected (n = 45), HoxB-9 injected (n = 36). (C) Q-PCR for HoxD1, A2, B4 and C6 in HoxD1 injected embryos. (D) Q-PCR for HoxB2, B4, B5 and A7 in HoxB4 GR injected embryos (activated at st.8). (E) Q-PCR for HoxB4, A7, C8 and B9 in HoxA7 injected embryos. (F) Q-PCR for HoxA7, B9, D10 and D13 in HoxB9 injected embryos.