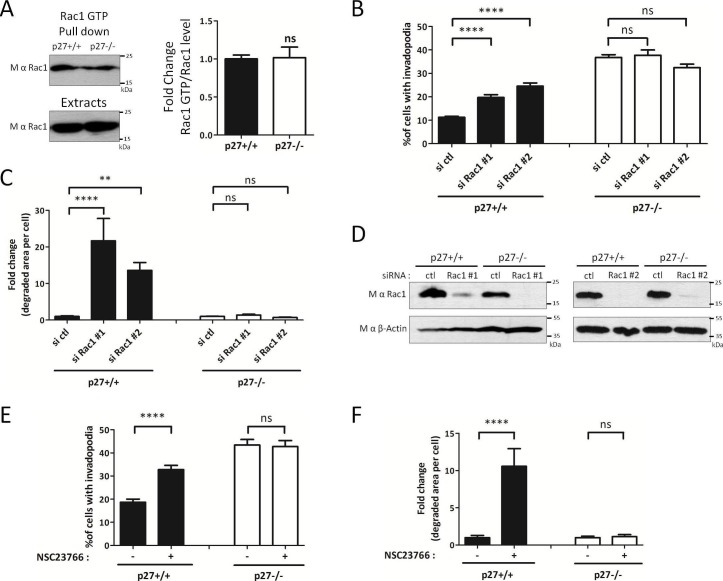
Figure 7. p27 regulates invadopodia formation downstream of Rac1.
(A) Cells were seeded for 24 hr and Rac1-GTP levels measured by GTP pull-downs assays using GST-PAK1-CD beads. The amounts of Rac1-GTP bound to the beads and of total Rac1 in the extracts were detected by immunoblot with mouse anti-Rac1. The graph shows the mean ratio of GTP-Rac1/total Rac1 from six independent experiments. (B–D) Cells were transfected with control (ctl) or Rac1 #1 or #2 siRNAs for 3 days. Cells were then seeded on Gelatin-A488 for 48 hr and for monitoring siRNA efficiency. Cells were stained with rabbit anti-Tks5 (M-300) to visualize invadopodia. At least ten fields per condition were used to count cells forming invadopodia, representing a minimum of 197 cells per genotype for each experiment (B) or to measure the area of degraded gelatin, expressed in fold-change compared to control siRNA treated conditions (C). (D) Rac1 silencing was evaluated by immunoblot with mouse anti-Rac1. β-actin was used as loading control. (E–F) Cells were processed as described in Figure 6D and E except that the Rac1 inhibitor NSC23766 at 100 μM was used instead of FRAX597. A minimum of 153 cells were counted per genotype for each experiment. (B–C; E–F) The graphs show the mean of at least three independent experiments. ****p<0.0001; **p<0.01.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.22207.028