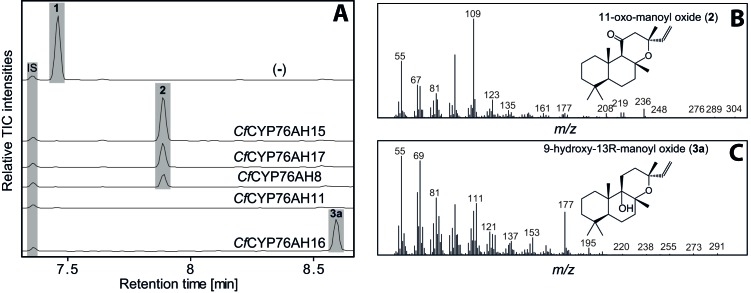
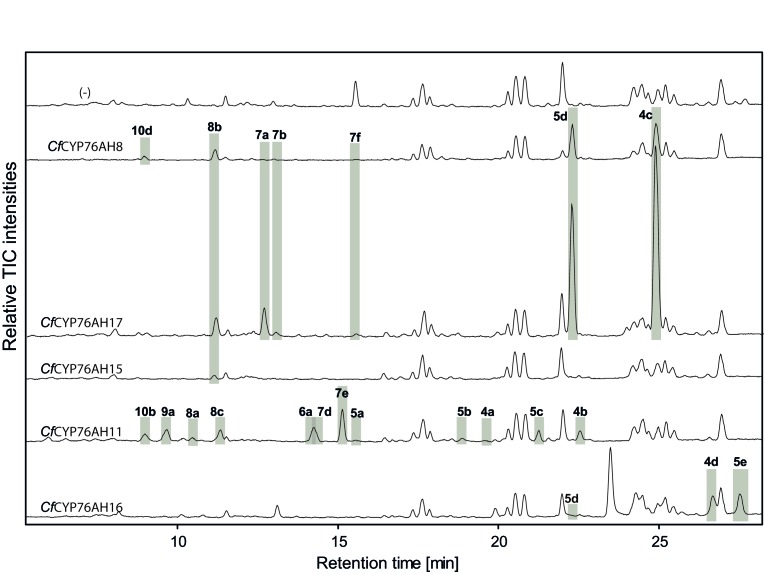
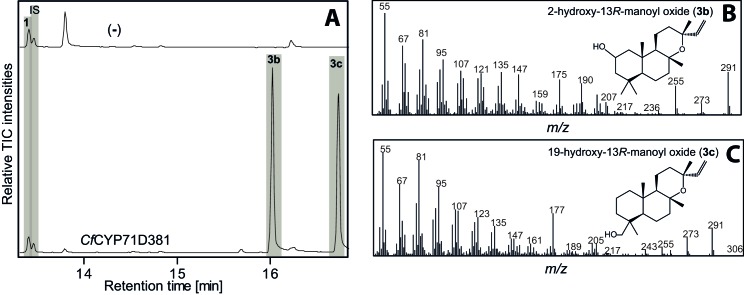
Figure 3. GC-MS analysis of 13R-manoyl oxide (1) derived diterpenoids obtained by transient expression of CYP76AHs from C.
forskohlii in N. benthamiana leaves. (A) GC-MS total ion chromatograms (TIC) of extracts from N. benthamiana transiently expressing CfCXS, CfGGPPS, CfTPS2 and CfTPS3 (13R-manoyl oxide biosynthesis) genes in combination with water (-), CfCYP76AH15, CfCYP76AH17, CfCYP76AH8, CfCYP76AH11 or CfCYP76AH16. 1-eicosene was used as internal standard (IS). 13R-manoyl oxide (1) was identified only in (-), indicating that it is further metabolized by the CfCYP76AH15, CfCYP76AH17, CfCYP76AH8, CfCYP76AH11 and CfCYP76AH16 enzymes. (B) m/z spectrum of 11-oxo-13R-manoyl oxide (2). (C) m/z spectrum of 9-hydroxy-13R-manoyl oxide (3a). The structure of both compounds was verified by NMR analysis (Tables 1 and 2). The compounds have been identified previously in C. forskohlii as putative intermediates in the in planta biosynthesis of forskolin (Asada et al., 2012). For each combination, extracts from leaves of three different N. benthamiana plants have been analyzed and representative chromatograms are shown.