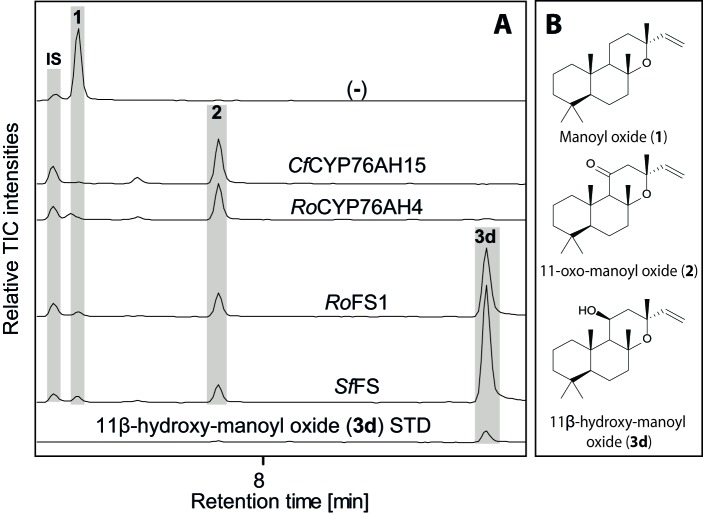
Figure 7. GC-MS analysis of 13R-manoyl oxide-derived diterpenoids obtained by transient expression of CYP76AHs in N. benthamiana leaves.
(A) Total ion chromatograms (TIC) of extracts transiently expressing CfCXS, CfGGPPS, CfTPS2 and CfTPS3 (13R-manoyl oxide biosynthesis genes) in combination with water (-), CfCYP76AH15, RoCYP76AH4, RoFS1 and SpFS are shown. 13R-manoyl oxide was observed in the (-) extracts, while 11-oxo-13R-manoyl oxide (2) was observed in the CfCYP76AH15, RoCYP76AH4, RoFS1 and SfFS extracts. 11-Hydroxy-13R-manoyl oxide (3d) is observed only in extracts expressing the RoFS1 and SfFS1 genes. Presence of 11-hydroxy-13R-manoyl oxide was verified by comparison to an authentic standard (Ignea et al., 2016b) while identification of 11-oxo-13R-manoyl oxide was confirmed by comparison of m/z spectra with a previously characterized compound (2). The results show RoCYP76AH4 has an activity similar to CfCYP76AH15, able to convert efficiently and specifically 13R-manoyl oxide to 2. RoFS1, as well as SfFS, can also convert 13R-manoyl oxide to 2 but they catalyze the synthesis of an additional product, 11-hydroxy-13R-manoyl oxide (3d). For every combination, extracts from leaves of three different N. benthamiana plants have been analyzed and representative chromatograms are shown.