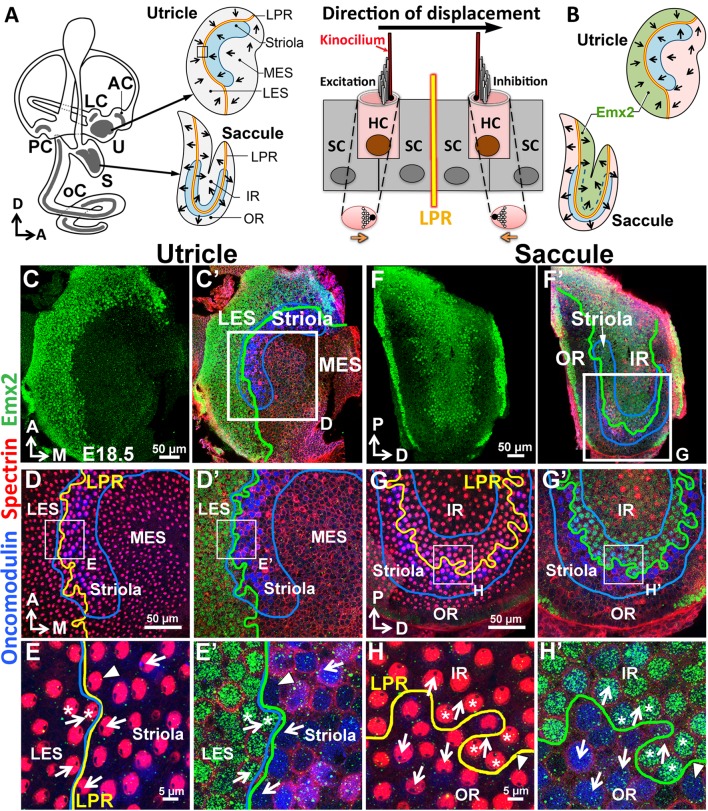
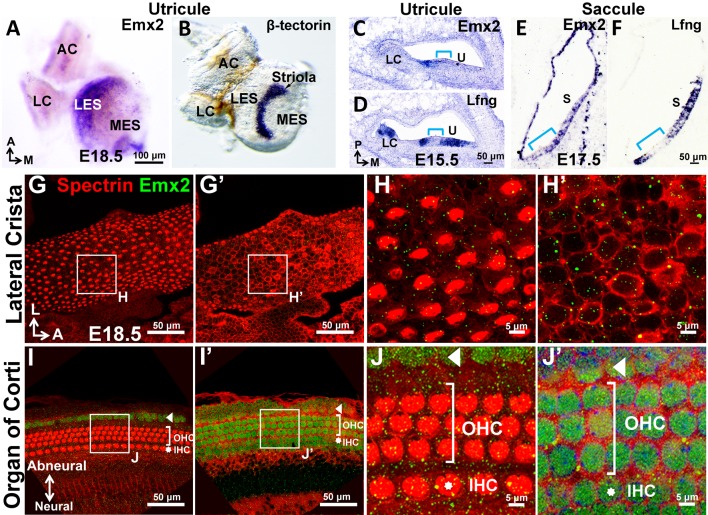
Figure 1. Regional expression of Emx2 in the maculae.
(A) Medial view of a mouse left inner ear with its six sensory organs (grey). Enlarged are the utricle and saccule showing their subdivisions, hair bundle polarity (arrows), LPR (yellow line), and striola (blue). The square denotes the sensory epithelium across the LPR on the right. Displacement of the hair bundle towards or away from the kinocilium results in depolarization and hyperpolarization of HC, respectively. (B) Schematic of the Emx2 expression domain (green) in the utricle and saccule. (C–H’) Utricle (C–E’) and saccule (F–H’) are stained for anti-Emx2 (green), anti-spectrin (red) and anti-oncomodulin (blue) antibodies (n = 6). Hair bundle polarity is determined by the location of the kinocilium, which is devoid of anti-spectrin staining (red). (D,E,G,H) and (D’,E’,G’,H’) are confocal images of the same HCs taken at the apical surface and nuclei level, respectively. (C,C’,D’,E’) Anti-Emx2 (green) staining is located in the lateral extrastriola (LES), which is lateral to the oncomodulin-positive striola (blue) of the utricle. Hair bundles in LES point toward those in the striola and medial extrastriola (MES) of utricle (E). (F,F’,G’,H’) Anti-Emx2 staining is restricted to the inner region (IR) of saccule and the LPR bisects the striola. Hair bundles in the IR point away from those in the outer region (OR) of saccule (H). The border of the Emx2-positive domain (green line, D’,E’,G’,H’) coincides with LPR (yellow line, D,E,G,H) in both maculae. Refer to Figure 2 for a description of asterisks and arrowheads. A, anterior; AC, LC, and PC, anterior, lateral and posterior crista; D, dorsal; M, medial; oC, organ of Corti; P, posterior; S, saccule; U, utricle.