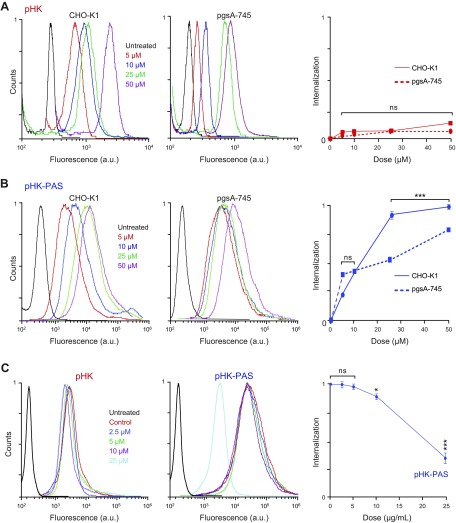
Figure 2.
Role of cell-surface proteoglycans in cellular uptake pHK and pHK-PAS. A, B) Wild-type CHO-K1 (left) and proteoglycan-deficient pgsA-745 (middle) cells were incubated with 5–50 µM pHKA488 (A) or pHK-PASA488 (B) in serum-free DMEM for 2 h. C) Effect of free heparin on peptide internalization. HeLa cells were pretreated for 30 min at 37°C in serum-free DMEM with extracellular heparin (0–25 μg/ml), then treated with 25 µM pHKA488 (left) or pHK-PASA488 (middle) and maintained for 2 h at 37°C in the presence of inhibitor and peptide. After peptide incubation, cells were washed 3 times with ice-cold PBS, trypsinized, centrifuged, and resuspended in ice-cold PBS with 10% FBS, and fluorescence was measured by FACS. Peptide internalization was determined by subtraction of background signal (cells treated with vehicle alone) from fluorescence intensities of peptide-treated cells and plotted relative to the maximum fluorescence intensity observed (right). (Error bars lie within the symbol for some data points.) ns, nonsignificant (P > 0.05). *P < 0.01, ***P < 0.0001 compared with controls.