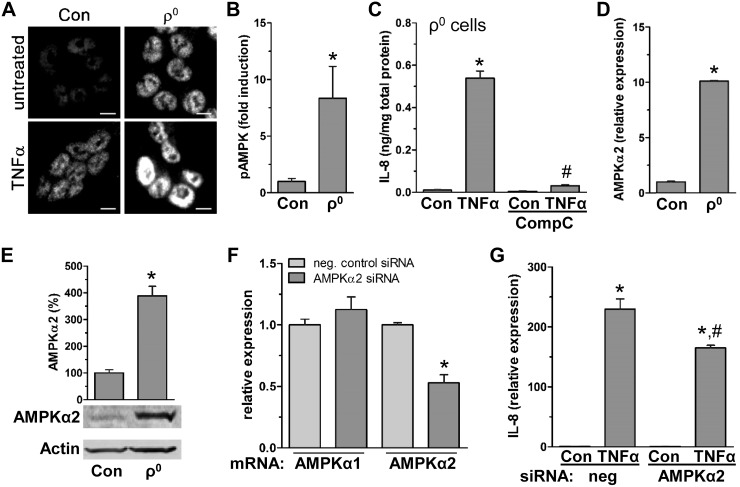
Figure 4.
TNF-α induced IL-8 is facilitated by reduced mitochondrial function via increased AMPK activity. A) HCT116 control (con) and ρ0 cells treated with TNF-α (15 min) were immunofluorescently stained for pAMPK (Alexa Fluor 594; representative image of 3 independent experiments). Scale bars, 5 µm. B) TNF-α-induced fold increase in ratio of pAMPK to total AMPK after immunoblotting of total protein from HCT116 con and ρ0 cells treated with TNF-α (15 min) (densitometric analysis; n = 3). *P < 0.05, compared to con, Student’s t test. C) In ρ0 cells, intracellular IL-8 was measured in presence of CompC after 4 h TNF-α treatment by ELISA (n = 3). *P < 0.05, compared to con; #P < 0.05compared to TNF-α alone, ANOVA. D, E) In HCT116 con and ρ0 cells, AMPKα2 subunit was quantified by qPCR (D) and immunoblot (E) (n = 3). *P < 0.05 compared to con, Student’s t test. F, G) As a control for specific silencing of AMPKα2, AMPKα subunits were quantified by qPCR (F), and IL-8 was quantified by qPCR in HCT116 con cells transfected with negative con (neg) and AMPKα2 siRNA in presence of TNF-α (2 h; n = 3) (G). *P < 0.05, compared to con; #P < 0.05 compared to TNF-α alone, Student’s t test, ANOVA.