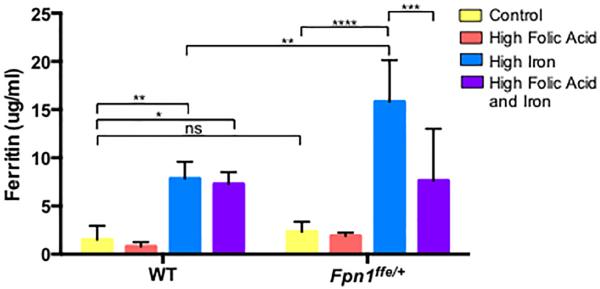
Figure 3. Supplementation with a high iron diet increases iron stores in wildtype and Fpn1ffe/+ dams.
Serum was obtained from pregnant dams upon dissection of embryos at 9.5 or 11.5 dpc. Dams were supplemented with control (yellow bar), high folic acid (10 ppm, orange bar), high iron (0.5% carbonyl iron, blue bar) or high folic acid and iron (purple bar) diets for 4 weeks before mating. Ferritin levels were determined by ELISA and served as a proxy for stored iron levels. Maternal serum ferritin was measured in 3 samples in the wildtype (WT) group and 5 in the Fpn1ffe/+ group. Statistical significance was determined by 2-factor ANOVA with post-hoc Sidak's multiple comparisons test. P-values ≤0.05 *, ≤0.01 **, ≤0.001 ***, ≤0.0001 **** or non significant (ns).