FIGURE 2.
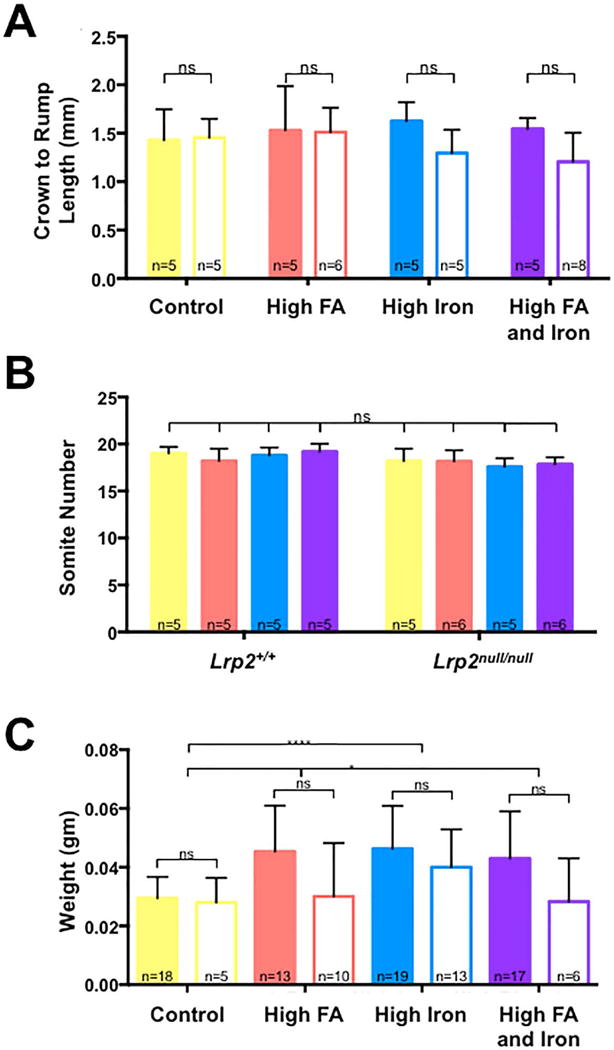
Effects of high iron and folic acid supplementation on growth of embryos. A: Comparison of crown to rump length (A) and somite numbers (B) between Lrp2null/null mutant embryos (no fill) and wild type (Lrp2+/+) littermates (filled) dissected at 9.5 dpc from Lrp2null/+ dams fed control (yellow), folic acid (FA; orange), high iron (blue) or high iron and folic acid (purple) supplemented diets. C: Comparison of weights of Lrp2null/null mutant embryos and wild type littermates dissected at 11.5 dpc from dams fed the indicated diets. Statistical significance was determined by two-factor ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. p-values: ≤0.05 (*), ≤0.0001 (****) or non significant (ns). An additional unpaired t-test was performed across the diets in (C). P-values are indicated as 0.012 (*), 0.0238 (*), or ≤0.0001 (****). The number of samples in each group is indicated.
