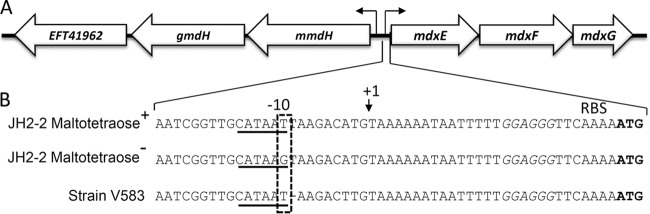
FIG 1.
The E. faecalis JH2-2 chromosomal region containing the mdxEFG and the upstream operon, which both contain genes required for maltodextrin utilization. (A) Presented are the three genes of the mdxEFG operon and the three upstream genes. They encode the two membrane components of the ABC transporter and the periplasmic binding protein and two α-glucosidases and a glucosyl transferase, respectively (P. Joyet, N. Sauvageot, A. Hartke, and J. Deutscher, unpublished data). The two operons are transcribed from two divergent promoters (small arrows). (B) A major part of our JH2-2 stock carries a mutation in the intergenic region leading to the replacement of the T in the sixth position of the −10 promoter region with a G (dashed box). The −10 promoter region of the mdxEFG operon is underlined, the transcription initiation point is marked with a small arrow, and the ribosome binding site (RBS) is written in italics. The start codon of mdxE is written in bold letters. The T-to-G mutation prevents the utilization of maltotetraose and longer maltooligosaccharides, as well as of panose and isopanose. The E. faecalis strain V583 and all other strains for which the genome has been completely sequenced, have the CATAAT −10 promoter sequence for the mdxEFG operon. However, these strains lack the T directly following the −10 promoter in JH2-2.