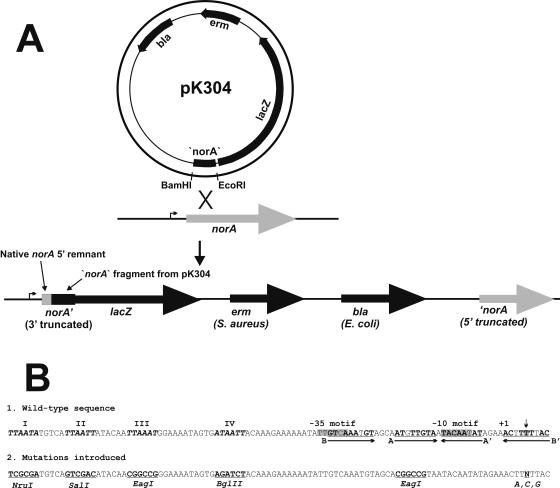
FIG. 1.
(A) Construction of the norA::lacZ fusion. In the presence of erythromycin, a single crossover at the site of homology between pK304 and the chromosome occurs, disrupting norA and transcriptionally fusing the norA promoter and about 400 bp of 5′ norA sequence with lacZ. erm expresses only in S. aureus, and bla expresses in E. coli. Truncated (3′ and 5′) refers to norA lacking 3′ and 5′ sequences, respectively. (B, 1) Wild-type norA promoter region and upstream sequence. Consensus TTAATT sequences are bold, italicized, and identified by Roman numerals, the −35 and −10 motifs and the +5 position of norA mRNA (site of flqB mutations) are highlighted (the +5 position is also noted by the downward arrow), the +1 position of norA mRNA is indicated, and the inverted repeats (A and B) are underlined and indicated by arrows. Perfectly matching bases in each repeat are in bold. (2) Mutations introduced into the norA promoter region by allele replacement.