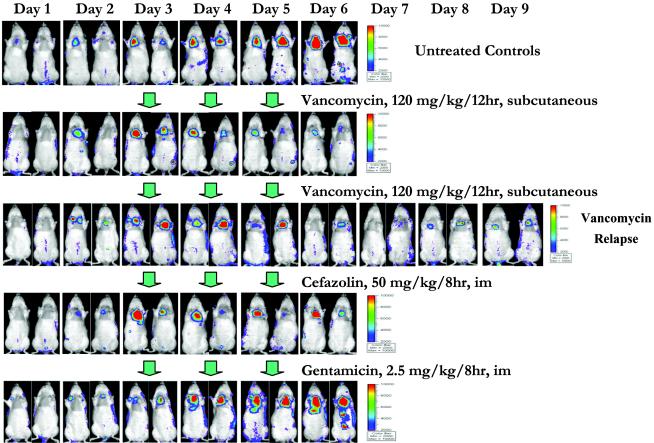
FIG. 5.
Real-time monitoring of the efficacy of vancomycin, cefazolin, and gentamicin in the experimental rat model of endocarditis due to S. aureus Xen29. Two representative animals from the untreated control and the antibiotic-treated groups are shown. Three days after infection with 105 CFU of S. aureus Xen29, the animals received either no antibiotics (untreated control), vancomycin (120 mg/kg every 12 h, subcutaneous), cefazolin (50 mg/kg every 8 h, i.m.), or gentamicin (2.5 mg/kg every 8 h, i.m.) for 3 days. Vancomycin relapse was studied 3 days after discontinuation of the treatment. The photon signals from all groups were monitored daily after infection by using the IVIS. The color bar indicates the signal intensity, with red and blue representing high and low bioluminescence, respectively.