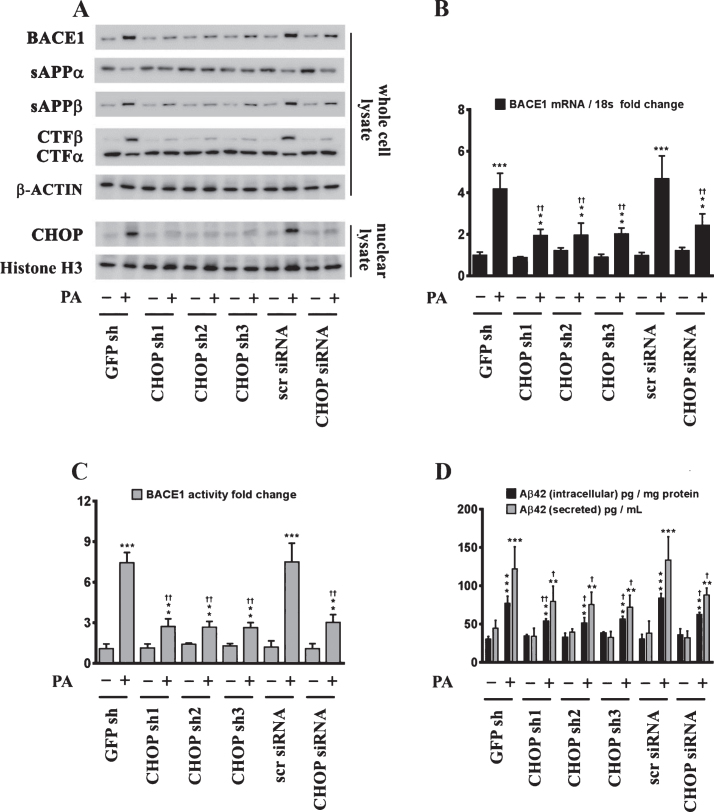
Fig.5.
CHOP mediates the palmitate-induced increase in BACE1 expression and subsequent Aβ genesis. A) Representative western blots show that knocking-down CHOP expression using a RNAi approach significantly attenuates the palmitate-induced increase in BACE1 protein levels accompanied by a decrease in the amyloidogenic processing of AβPP as evidenced by a decrease in the palmitate-induced increase in sAβPPβ and CTFβ levels concomitant with an increase in the palmitate-induced decrease in sAβPPα and CTFα levels in the whole cell homogenates from SH-SY5Y-APPSwe cells. B, C) Knocking-down CHOP expression attenuates the palmitate-induced increase in BACE1 mRNA expression (B) and BACE1 activity (C) in SH-SY5Y-APPSwe cells. D) ELISA immunoassays show that knocking-down CHOP expression significantly mitigates the exogenous palmitate treatment-induced increase in the levels of the intracellular Aβ1 - 42 species in the whole cell lysates and secreted Aβ1 - 42 species in the conditioned media, from SH-SY5Y-APPSwe cells. Data is expressed as Mean±S.D and includes determination made in four (n = 4) separate cell culture experiments. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 versus BSA-treated GFP knock-down cells or BSA-treated scrambled siRNA transfected cells; †p < 0.05, ††p < 0.01, versus palmitate-treated GFP knock-down cells or palmitate-treated scrambled siRNA transfected cells. PA, palmitic acid.