Fig. 1.
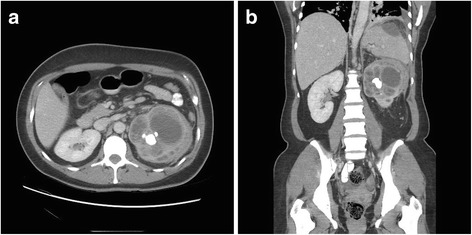
Computed tomography of the abdomen and pelvis demonstrating xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis of the left kidney. a Axial section at the level of the renal calyces demonstrating markedly abnormal appearance of the left kidney. The renal pelvis is contracted around a staghorn calculus with surrounding distension and ballooning in the upper pole calyces, with surrounding soft tissue stranding and enlarged perinephric and retroperitoneal lymph nodes which are presumed to be reactive. b Coronal section of the abdomen and pelvis showing aforementioned changes in the left kidney with superior extension into the spleen parenchyma. Tracking of the inflammatory perinephric soft tissue along the posterior aspect of the spleen (not shown in this view) connects with a large hypodense collection under the splenic capsule, which also appears to communicate across left hemidiaphragm with resulting left-sided pleural effusion
