Fig. 6.
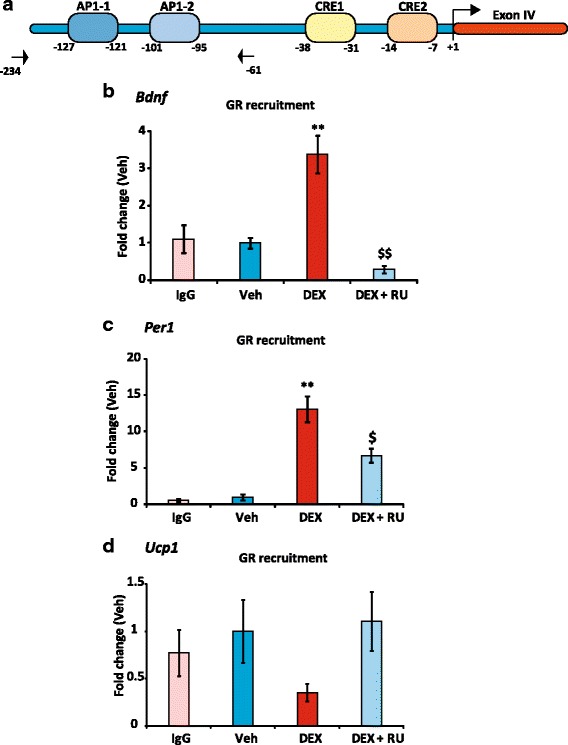
GR recruitment on Bdnf DNA sequence. a, Schematic representation of a short fragment upstream of exon IV that contains the two potential AP1 binding sites, AP1-1 and AP1-2 as well as two potential cAMP Response-Elements CRE-1 and CRE-2 according to the Jaspar database. Exon IV transcription start site is set at +1. Primers for ChIP are indicated by arrows. b, ChIP-qPCR results showing GR recruitment upstream of exon IV region in BZ cells after treatment with DEX (10-7 M) or DEX together with RU (10-6 M) for 1 h. IgG: ChIP-qPCR with IgG negative control antibodies on the same sequence. Results of 3 different experiments are pooled setting the vehicle mean value at 1 (n = 6, Mean ± SEM), and showed as fold change of the percentage of input value of Veh.** P < 0.01, DEX vs Veh; $$ P < 0.01, DEX + RU vs DEX; Mann Whitney U-tests. c, ChIP-qPCR results (same samples than in B) of GR recruitment on Per1 gene regulatory sequence used as positive control in BZ cells under DEX or DEX + RU treatment for 1 h. ** P < 0.01, DEX vs Veh. $ P < 0.05, DEX + RU vs DEX. d, same as in (c) with GR recruitment on Ucp1 gene used as negative control. Primers for genomic PCR amplification are listed in Additional file 1: Table S1
