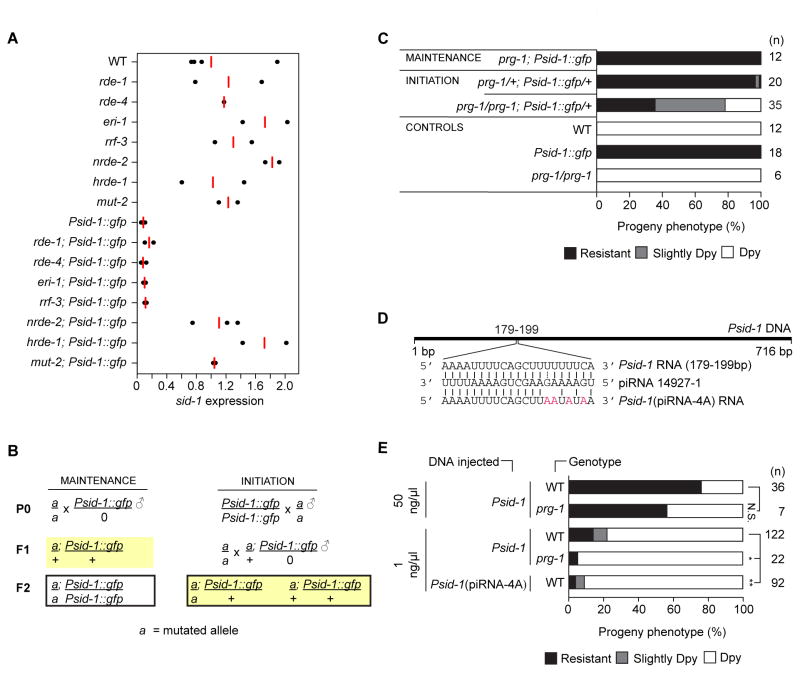
Figure 4. Genetic requirements for sid-1 silencing.
(A) sid-1 mRNA expression in mixed stage worms. Average (red bar) of biological replicates relative to gpd-2/3. (B) Maintenance and initiation crosses (silencing competent hermaphrodite germline is highlighted). (C) RNAi sensitivity of progeny of (n) F2 L4 larvae produced by crosses in (B). (D) Putative piRNA 14927-1 binding site and mutant Psid-1(piRNA-4A) sequence. (E) RNAi sensitivity of progeny of (n) F2 lines produced by injected wild-type or piRNA-4A Psid-1 DNA. N.S. = Not significant, * = p < 0.05, ** = p < 0.002 (Mann-Whitney test). Resistant and slightly Dpy values were combined for statistics. In A–C, the Psid-1::gfp array is integrated on the X chromosome. See also Figure S4.