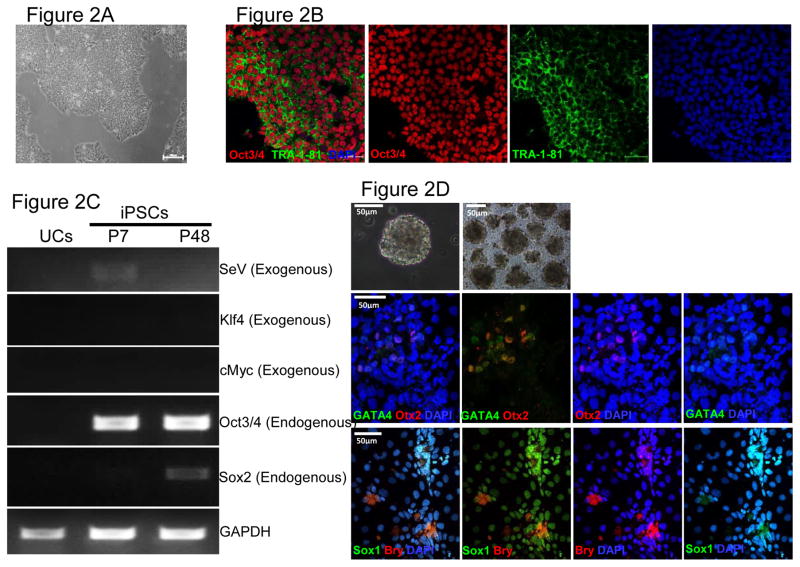
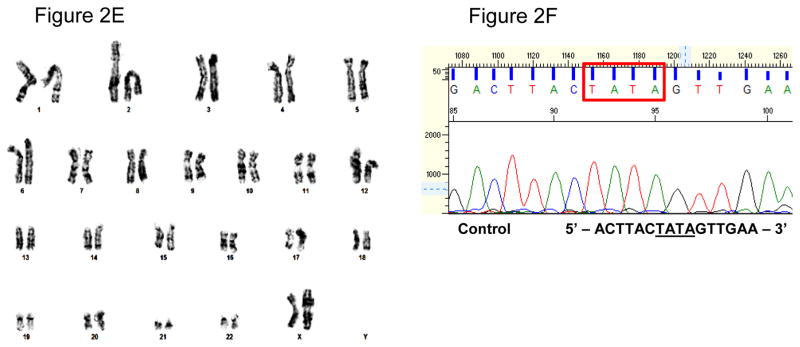
Figure 2. Characterization of iPSCs and genotypic evaluation.
(A) Phase contrast micrograph of the cultured iPSC clone, plated under feeder-free conditions on matrigel. Scale bar, 50μm. (B) Pluripotency of iPSCs confirmed by immunostaining with Oct3/4 (Red) and TRA-1-81 (green) markers and counterstained nuclei with blue DAPI stain. Scale bar, 50μm. (C) RT-PCR gene expression analysis show upregulation of endogenous pluripotent genes (Oct3/4 and Sox2) and elimination of the non-integrating viral genome and exogenous genes (SeV, Klf4 and cMyc). (D) Differentiation into three embyonic germ layers was confirm after processing iPSCs to form embryoid bodies (EBs) and allowing spontaneous in vitro differentiation. Ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm characterized by immunostaining with Otx 2 (Red)/SOX1 (Green), Brachyury (Red), and GATA4 (Green), respectively. Scale bar, 50μm. (E) Karyogram of iPSCs demonstrate normal ploidy of a female subject. (G) Electropherogram confirms the wild-type gene sequence on the exon 4 of PAI-1 gene in control iPSCs (iPAI-005-B).