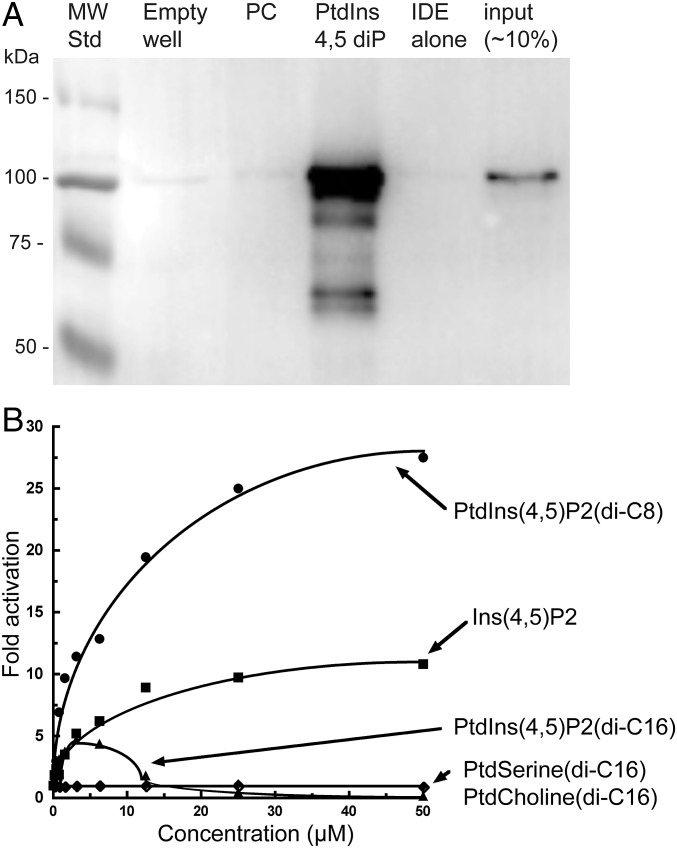
Fig. 3.
IDE binds to phosphatidylinositol-containing liposomes and PtdIns(4,5)P2 activates the enzyme. (A) IDE binding to liposomes was tested using 260 μg of total lipid and 0.9 µg of IDE. Liposomes isolated after incubation were separated on a polyacrylamide gel and stained by Western blotting with anti-IDE antibody. Lane 1 (MW Std), molecular weight markers; lane 2 (empty well), no IDE or liposomes; lane 3 (PC), IDE plus liposomes containing only DOPC; lane 4 (PtdIns 4,5 diP), IDE plus DOPC liposomes with PtdIns(4,5)P2 at a ratio of 10:1; lane 5 (IDE alone), enzyme only; lane 6 (input), 0.1 µg of purified IDE without incubation. (B) Comparison of IDE activation by PtdIns(4,5)P2 (di-C16 or di-C8 acyl chains), Ins(4,5)P2, phosphatidylserine, and phosphatidylcholine. IDE activity was measured by the hydrolysis of Abz-GGFLRKHGQ-Eddnp substrate at varying concentrations of the indicated lipid or Ins(4,5)P2. The curves for activation by PtdIns(4,5)P2 (di-C8 acyl chains) and Ins(4,5)P2 are the fits to a hyperbolic function. Curves are drawn through the data points for activation by other compounds to show trends.