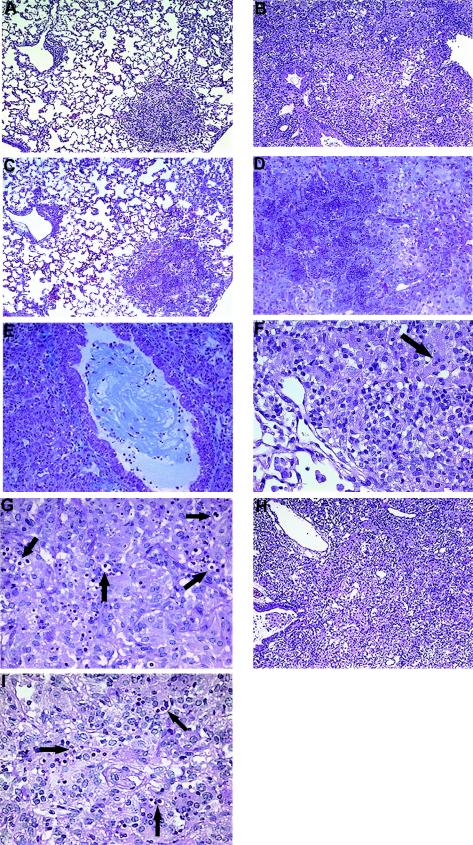
FIG. 2.
Photomicrographs of lungs from C. neoformans-infected, anti-TNF-α-treated, and imDC-treated mice at week 7. (A) Control C. neoformans-infected mouse. Note that only a small focus of inflammation is detected at week 7. (B) Anti-TNF-α-treated C. neoformans-infected mouse. Note the consolidation due to the overwhelming inflammatory response. (C) Control C. neoformans-infected lung demonstrating minimal collagen deposition. (D) Necrotic area in the lung of an anti-TNF-α-treated mouse demonstrating marked collagen deposition. (E) An airway in the lung of an anti-TNF-α-treated mouse significantly obstructed by collagen. (F) The presence of intracellular cryptococci (arrow) is minimal in the inflammatory sites in the lung of a control C. neoformans-infected mouse. (G) Detection of significant numbers of intracellular cryptococci (arrows) in the lung of an anti-TNF-α-treated mouse. (H) Lung of an imDC-treated C. neoformans-infected mouse. Note the consolidation due to the inflammatory response. (I) Detection of significant numbers of intracellular cryptococci (arrows) in the lung of an imDC-treated mouse. (A, B, H) Hematoxylin and eosin. Magnification, ×54. (C-E) Trichrome. Magnification, ×108. (F, G, I) PAS. Magnification, ×216.