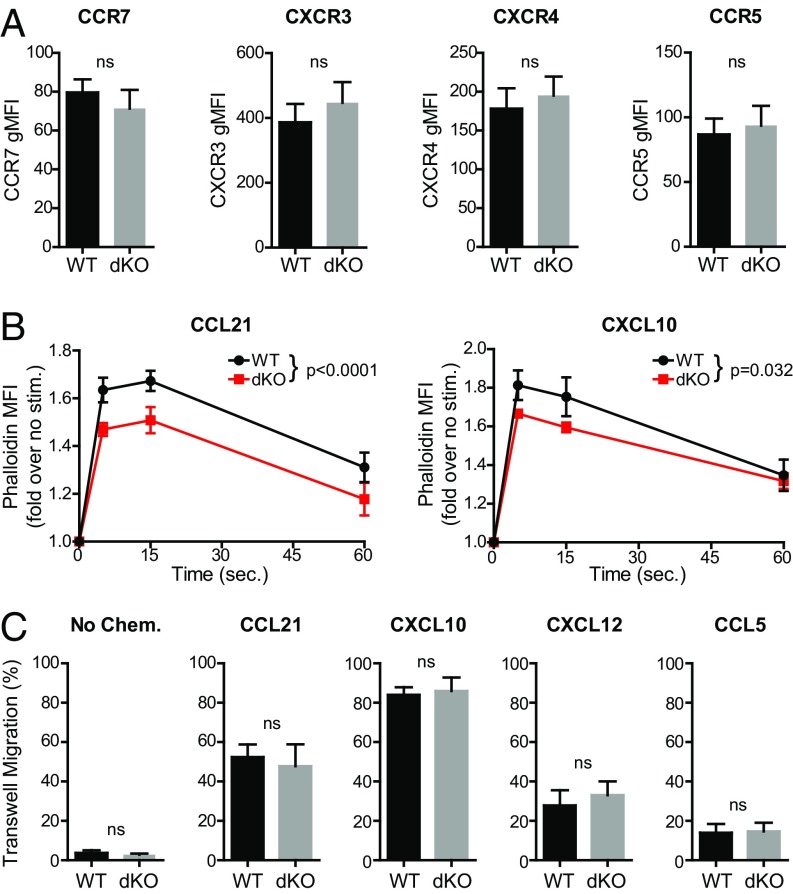
Fig. 3.
Deletion of both EVL and VASP in activated CD4 T cells reduces chemokine-triggered actin polymerization but does not impair chemotaxis. (A) Quantification of chemokine receptor expression in WT and EVL/VASP dKO activated T cells; data shown as gMFI. (B) Time-course analysis of actin polymerization in WT and dKO activated T cells in response to 100 ng/mL CCL21 stimulation (WT vs. dKO curve comparison P < 0.0001) or 100 ng/mL CXCL10 stimulation (WT vs. dKO curve comparison P = 0.032), measured by flow cytometry quantification of fluorescent phalloidin staining. (C) Chemotactic migration across 5-μm pore Transwell chambers in the absence of chemokine, or in the presence of CCL21 (100 ng/mL), CXCL10 (100 ng/mL), CXCL12 (1 μg/mL), or CCL5 (100 ng/mL) in the bottom wells as indicated. Data are the average of at least three independent experiments; error bars are SEM; statistics are paired t tests in A and C, or two-way ANOVA in B. ns, not significant.