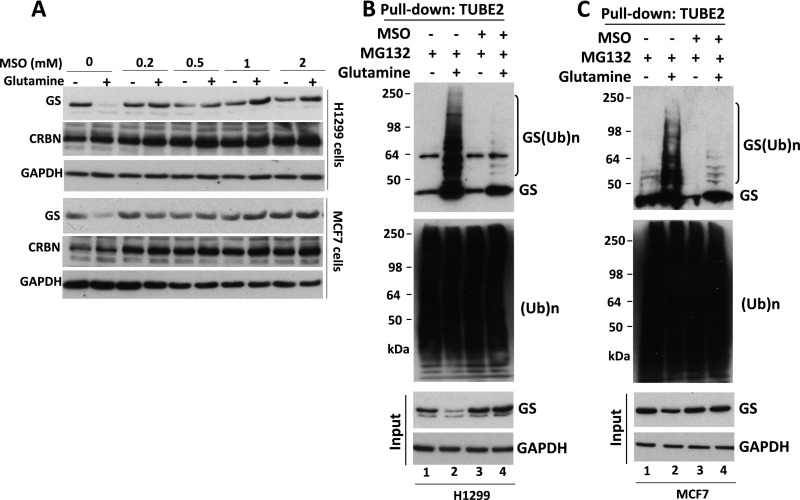
Fig. S1.
(Related to Fig. 1) The GS inhibitor MSO suppresses glutamine-induced GS ubiquitylation and degradation. (A) H1299 and MCF7 cells were starved of glutamine for 24 h. Cells were pretreated with the GS inhibitor MSO for 30 min, followed by the addition (or not) of 4 mM glutamine for 8 h. Cell extracts were analyzed by SDS/PAGE and immunoblotting with antibodies against GS, CRBN, and GAPDH. (B and C) H1299 (B) and MCF7 (C) cells were starved of glutamine for 24 h and then were pretreated with MG132 (10 μM) in the presence or absence of MSO (1 mM) for 30 min, followed by the addition (or not) of 4 mM glutamine for 3 h. Cell lysates were fractionated on a TUBE2 resin. The bound fractions and lysate samples (inputs) were analyzed by SDS/PAGE and immunoblotting with antibodies against GS, ubiquitin, and GAPDH. (Ub)n, polyubiquitin.