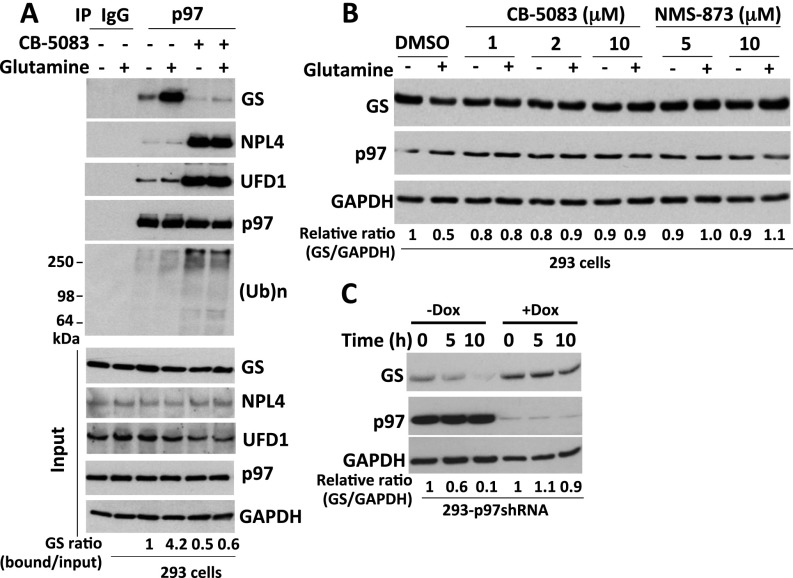
Fig. S2.
(Related to Fig. 2) p97 interacts with endogenous GS and is required for glutamine-induced GS degradation. (A) HEK293 cells were starved of glutamine for 24 h and were pretreated (or not) with CB-5083 (10 μM) for 30 min, followed by the addition (or not) of 4 mM glutamine for 2 h. Protein extracts were immunoprecipitated with mouse IgG control or p97 antibodies, followed by Western blot analysis with the indicated antibodies. The ratios of GS bound to p97 normalized to input GS are shown. (Ub)n, polyubiquitin. (B) HEK293 cells were starved of glutamine for 24 h and were pretreated with the p97 inhibitor NMS-873 or CB-5083 for 30 min, followed by the addition (or not) of 4 mM glutamine for 4 h. Cell extracts were analyzed by SDS/PAGE and immunoblotting with antibodies against GS, p97, and GAPDH. The relative ratio of GS:GAPDH, normalized to lane 1, is shown. (C) HEK293 cells stably expressing doxycycline (Dox)-inducible shRNA targeting p97 were mock-treated or were induced with doxycycline (1 µg/mL) for 48 h and then were starved of glutamine for 24 h, followed by the addition of 4 mM glutamine and the HDAC inhibitors (2 μM SAHA+10 mM NAM) for the indicated times. Cell extracts were analyzed by SDS/PAGE and immunoblotting with antibodies against GS, p97, and GAPDH. The GS:GAPDH ratio for each sample was calculated, normalized to untreated cells, and is indicated below the bottom immunoblot in each panel.