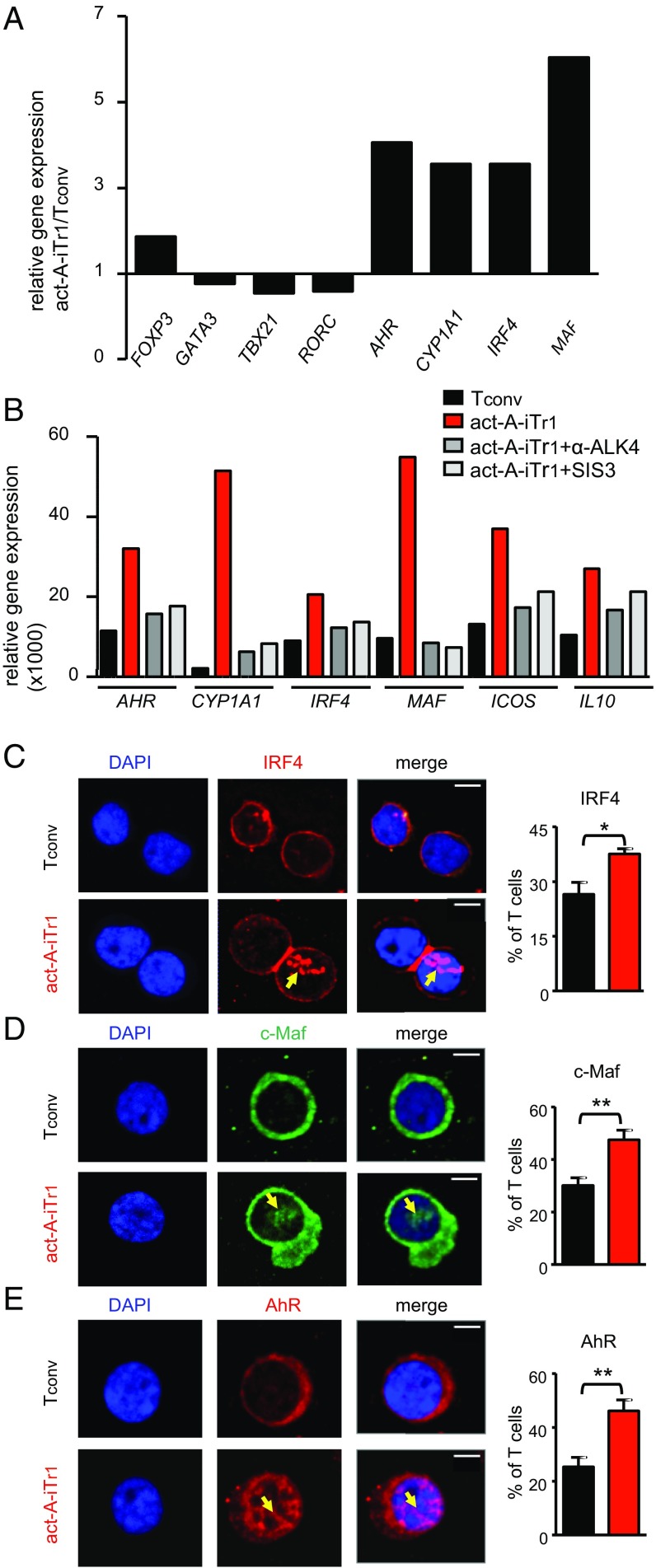
Fig. 3.
IRF4, AhR, and c-Maf are activated upon stimulation of human CD4+ T cells with activin-A. (A) Human naive CD4+ T cells were stimulated with allergen-loaded, mitomycin-treated APCs in the presence of PBS or activin-A for 3 d. Real-time PCR analysis of the indicated genes is shown. Results are representative of n = 4 separate experiments (n = 4 donors) and were normalized to GAPDH. (B) Tconv or act-A–iTr1 cells were generated as above with an anti-ALK4 blocking antibody or the Smad3 inhibitor, SIS3. Real-time PCR results are shown relative to GAPDH. Data are representative of n = 4 independent experiments (n = 4 donors). (C–E) Confocal microscopy images of Tconv or act-A–iTr1 cells stained with fluorescently conjugated anti-AhR, anti-IRF4, and anti–c-Maf antibodies. Nuclei are stained blue with DAPI. (Scale bars: IRF4 images, 4 μm; AhR and c-Maf images, 2 μm). Cumulative data showing the percentages of AhR+, IRF4+, or c-Maf+ T cells were pooled from n = 4 independent experiments (n = 4 donors). Statistical analysis was performed by a nonparametric (Mann–Whitney) unpaired Student’s t test (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01).