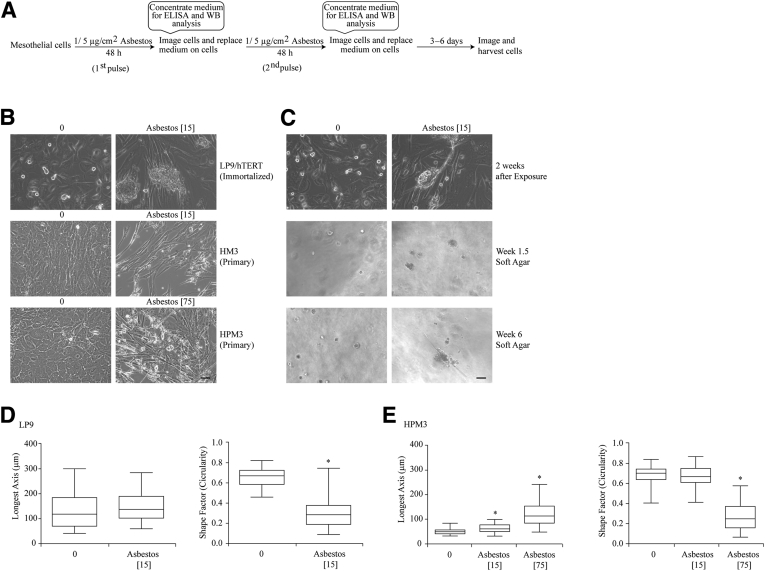
Figure 1.
Asbestos (Asb) exposure induces a morphologic change in human mesothelial cells. A: Schematic representation of Asb exposure schedule for induction mesothelial to fibroblastic transition. B: Exposure of LP9, HM3 (peritoneal), and HPM3 (pleural) cells to Asb (1 [peritoneal cells] [15 × 10−6 μm2/cm2 (Asb 15)] and 5 μg/cm2 [75 × 10−6 μm2/cm2 (Asb 75)] [pleural cells]) for 2 weeks and 1 week, respectively, resulted in morphologic changes to the cells during exposure. C: Fibroblastic-looking LP9 cells from B were grown on soft agar to determine whether the cells were transformed and capable of forming colonies. All micrographs were imaged on Olympus IX70 inverted microscope. D and E: Quantitative depiction of morphologic changes of LP9 (D) and HPM3 (E) cells as determined using the MetaMorph image analysis software version 7.8.9.0. The integrated morphologic and regional measurement tools were used to determine the shape factor (circularity) and longest axis (length) of cells, respectively. Numbers in brackets denote surface area concentrations of asbestos. ∗P < 0.05 versus control. Scale bars = 50 μm (B and C). ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; WB, western blot.