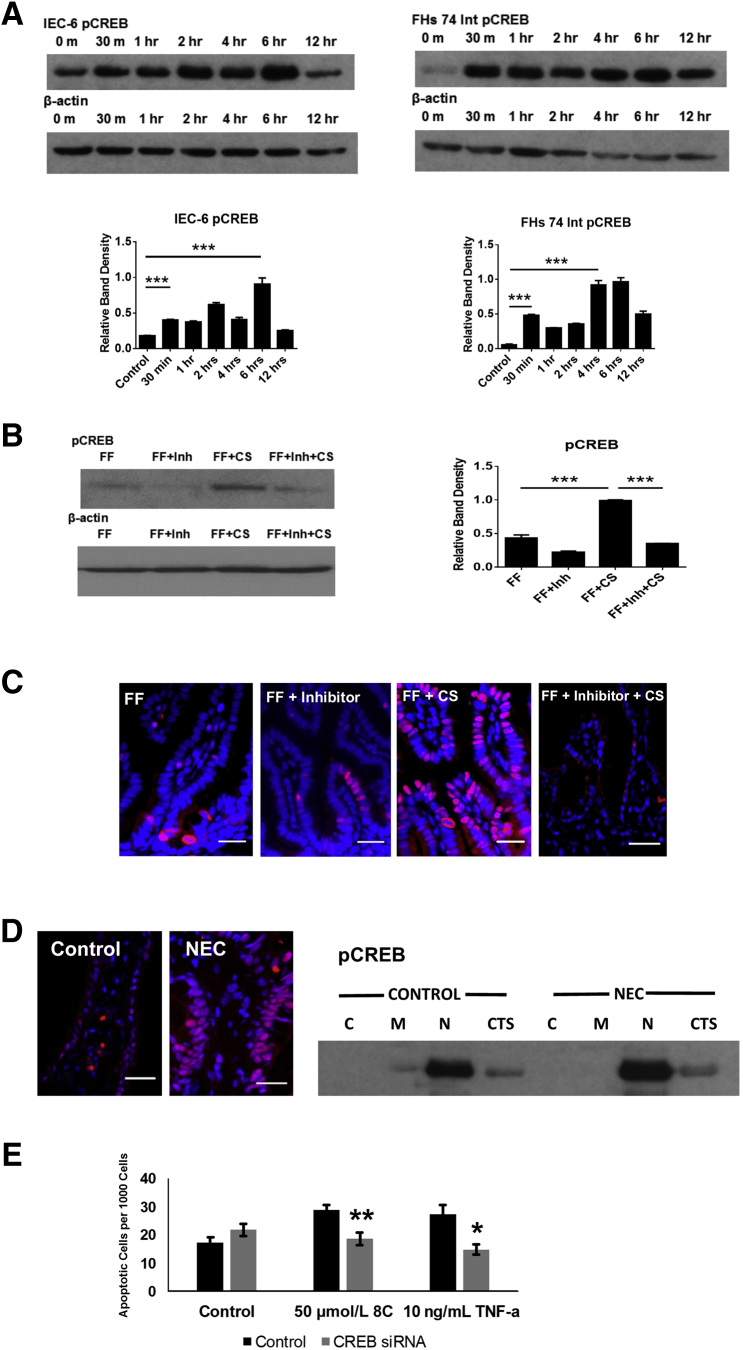
Figure 5.
A: CREB is activated in IEC-6 and FHs 74 Int cells after infection with CS. IEC-6 and FHs 74 Int cells were grown and infected with CS. Cell lysates were collected and pCREB was measured by Western blot analysis. pCREB was significantly higher than controls by 30 minutes and again at 6 hours in the IEC-6 cells. pCREB was also significantly higher than controls by 30 minutes and 4 hours in the FHs 74 Int cells of infection with CS. B: CREB was activated in experimental NEC and was diminished in the presence of a PKA inhibitor. After 4 days of FF and H, rat pups were sacrificed and intestine was harvested. Protein isolated was isolated from whole intestine samples. Western blot analysis revealed increased CREB phosphorylation in pups with CS-induced NEC compared with sterile FF controls. Pups that received a pretreatment of KT5720 had reduced CREB phosphorylation, despite the presence of CS. A representative Western blot analysis is shown. β-actin was stable. C: CREB is activated within the intestinal epithelium after CS exposure. Rat pup intestine was harvested and stored in OCT media at −80°C. Frozen sections were stained by immunofluorescence for pCREB. Imaging demonstrated increased active CREB signal in the epithelium (red stain) of rat pups fed CS-inoculated formula. This staining was less pronounced in control animals that received sterile formula (data not shown) and those pups that received a pretreatment of KT5720 (FF + Inh + CS). The blue cells are stained with DAPI. D: CREB is activated within the epithelium of human patients with active NEC. Human tissue was harvested and stored at −80°C. Frozen sections were stained by immunofluorescence for pCREB. Imaging demonstrated increased active CREB signal in the epithelium (red stain) of human patients with active NEC. The blue cells are stained with DAPI. E: CREB knockdown is protective against cAMP analogue and TNF-α–induced intestinal epithelial apoptosis. IEC-6 cells were grown on chamber slides and transfected with control siRNA or CREB siRNA. Cells were treated with doses of a cAMP analogue (8C) or TNF-α at doses to induce apoptosis. Cells were stained with DAPI and ApoTag, and apoptotic cells were quantified. CREB knockdown decreased the amount of apoptotic cells after treatment with 8C or TNF-α (P = 0.0017 and P = 0.016, respectively). Data are expressed as means ± SEM. n = 10 pups per group. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗P < 0.001. Scale bars = 25 μm. C, cytosol; CREB, cAMP response element binding protein; CS, Cronobacter sakazakii; CTS, cytoskeleton; FF, formula fed; H, hypoxia; HFs 74 Int, human small intestinal cell line; IEC-6, rat intestinal epithelial cell line; Inh, inhibitor; M, membrane; N, nuclear; NEC, necrotizing enterocolitis; OCT, optimal cutting temperature; pCREB, phosphorylated CREB; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor α; 8C, 8-(-4-Chlorophenylthio)-2′-O-methyladenosine 3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate monosodium.