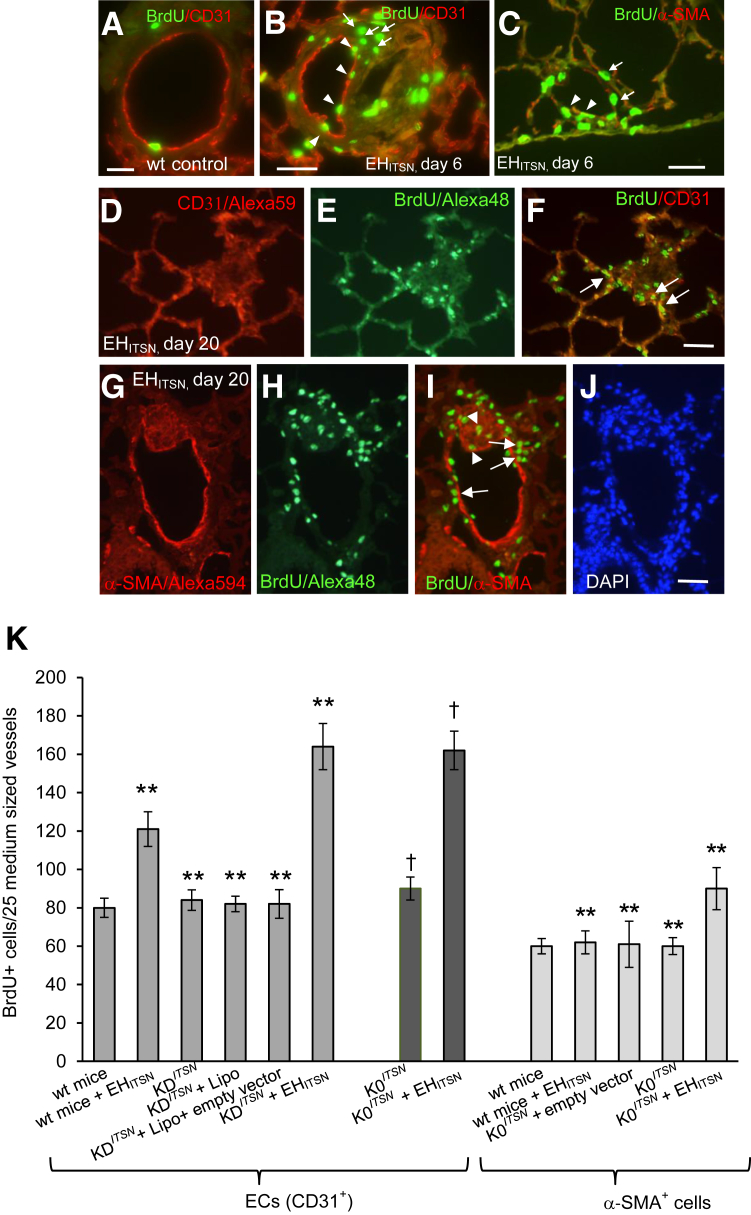
Figure 2.
Myc-EHITSN expression in K0ITSN+/− murine lungs triggers proliferation of endothelial cell (EC) and α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA)+ lung resident cells. A–C: Wild-type (wt) (A) and myc-EHITSN-transduced mice, day 6 of treatment, were subjected to bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) assay, followed by BrdU–fluorescein isothiocyanate and CD31 Alexa Fluor 594 (B) or α-SMA Alexa Fluor 594 (C) antibody immunohistochemistry for positive identification of ECs and myofibroblasts, smooth muscle cells, and undifferentiated cells, respectively. Representative micrograph illustrates the BrdU/CD31 colocalization (B, arrowheads) as well as significant proliferation of other lung resident cells (B, arrows). C: α-SMA+/BrdU colocalization (arrowheads) within the wall of a pulmonary arteriole or their close proximity (arrows) was also detected. D–I: Representative CD31/BrdU (D–F) and α-SMA+/BrdU (G–I) immunohistochemistry of lung sections of myc-EHITSN-transduced K0ITSN+/− mouse lung sections, day 20 of treatment, illustrates clusters of proliferative cells [ECs and α-SMA+ cells (F and I, arrows, respectively)], as well as other lung resident cells (frequently detected in vascular lesions that obliterate the vessel lumina; I, arrowheads). J: DAPI staining illustrates the hypercellularity associated with the remodeled vessel. K: Quantification of the number of BrdU+ ECs and BrdU+/α-SMAs+ in the mid-sized lung vessels of controls versus EHITSN-treated mice. All data shown are representative of four different experiments with three mice for the control groups and five mice per experimental condition. Wt mice include CD1 as well as 129SV/J genetic background mice. No significant differences were noticed in proliferation of α-SMAs+ between wt mice, untreated KDITSN, and K0ITSN+/− mice. n = 3 mice per group in three independent experiments (A–C); n = 12 (J); n = 4 different experiments (K); n = 3 mice for the control groups (K); n = 5 mice per experimental condition (K). ∗∗P < 0.01 versus wt mice; †P < 0.05 versus K0ITSN+/− mice. Scale bars: 20 μm (A–C); 25 μm (D–F); 40 μm (G–J).