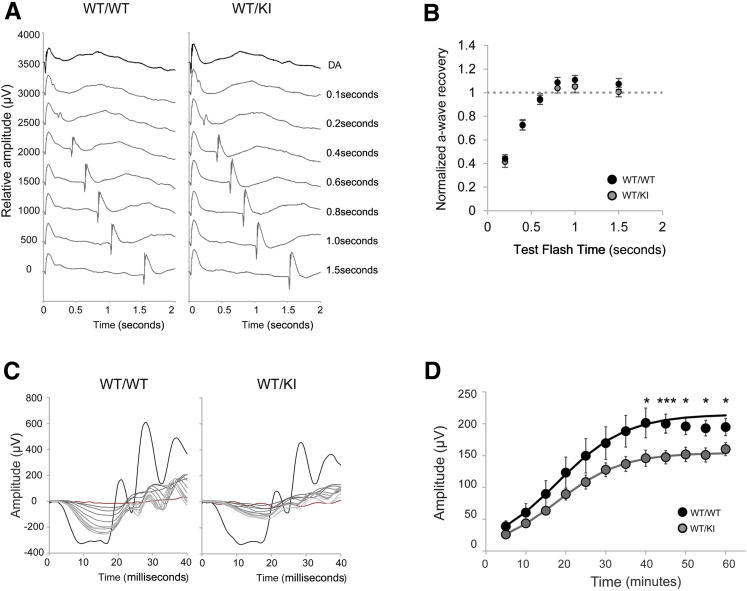
Figure 6.
Analysis of visual chromophore regeneration. A: Double-flash electroretinography (ERG) on WT/WT and WT/KI mice. Fully dark-adapted mice were subjected to single flash (4 cd·s/m2), followed by test flashes (40 cd·s/m2) at various delay times. Representative waveforms from each genotype are shown. B: Normalized amplitude of A-wave from WT/WT and WT/KI mice are shown. A-wave amplitude generated from each test flash was normalized by a fully dark-adapted A-wave amplitude. C: Dark-adaptation recovery ERG examining the A-wave value. Mice in indicated groups were bleached at 1000 cd/m2 for 2 minutes, followed by 60 minutes of rest in the dark. A single-flash ERG response at 10 cd·s/m2 was acquired every 5 minutes. Representative waveforms from each genotype are shown. Black and red traces are before and after bleach ERG responses, respectively. Response from each time point is depicted in varying shades of gray. D: Averaged recovering A-wave amplitudes of WT/WT and WT/KI mice are shown. Data were fitted using a nonlinear regression curve with previously published formula.32 Data are given as means ± SEM (B and D). n = 6 (B, WT/WT); n = 8 (B, WT/KI); n = 10 (D, WT/WT); n = 16 (D, WT/KI). ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗∗P < 0.001 (t-test). KI, knock in; WT, wild type.