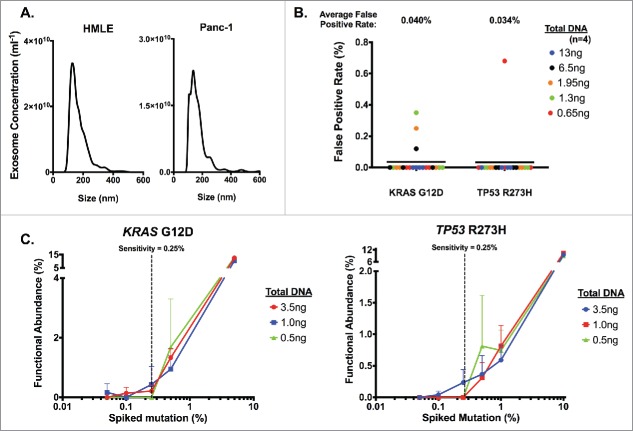
Figure 1.
Definition of digital PCR parameters using cell line-derived exosomal DNA. Exosomes were pelleted from HMLE and Panc-1 cell culture supernatant with sequential filtration and ultracentrifugation, and DNA was extracted from purified exosomes. (A) Concentration and size distribution of HMLE (left) and Panc-1 (right) cell-derived exosome were analyzed using nanoparticle tracking analysis. (B) Determination of the average false positive rate using HMLE exosomal DNA. ng: nanograms. (C) Determination of the sensitivity threshold by measuring the relative functional abundance of titrated mixture of Panc-1 exosomal DNA spiked in HMLE exosomal DNA samples. Defined percentages of spiked Panc-1 exosomal DNA (with KRASG12D mutation and TP53R273H mutation) with HMLE exosomal DNA were expressed as an expected percentage of spiked mutation, and dPCR analyses were run using the listed amount of DNA input (n≥ 2 for all other points except n = 1 for 5% in KRASG12D and 10% in TP53R273H). The sensitivity threshold was set to 0.25% to reliably detect either KRASG12D (left) or TP53R273H (right) mutations.