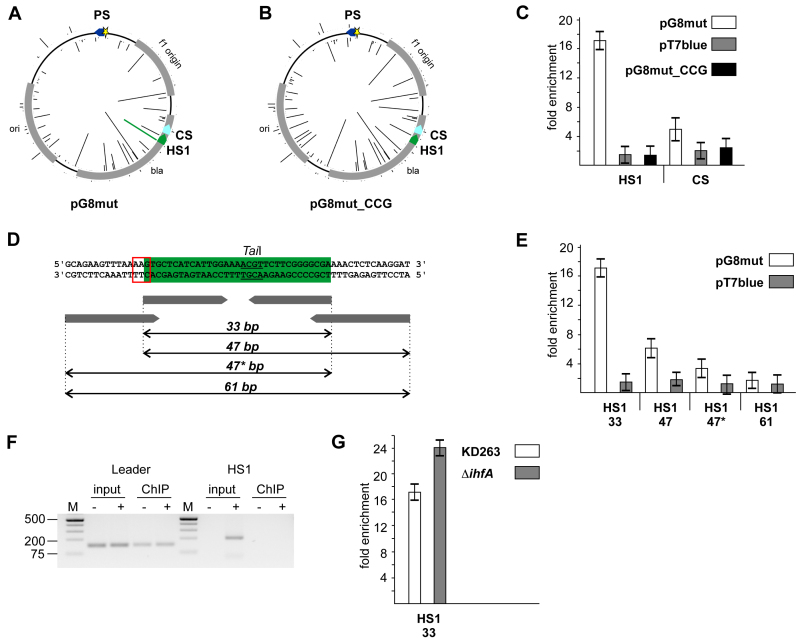
Figure 2.
Cas1 is associated with hot protospacers in target DNA during primed adaptation. (A, B) Spacers acquired by KD263 cells transformed with pG8mut (A) and pG8mut_CCG (B) plasmids. The priming G8 protospacer is shown as a blue arrow with an asterisk indicating mutation introducing a mismatch with G8 crRNA spacer. The heights of the bars emanating from circles representing each plasmid indicate the relative efficiency of protospacer use (number of times reads with matching acquired spacers were observed). CS and HS1 are, correspondingly, cold and hot protospacers. In A, the bar indicating the efficiency of spacer acquisition from the HS1 protospacer is highlighted in green. No spacers from HS1 were acquired from pG8mut_CCG (B). (C) Results of Cas1 ChIP analysis with primer pairs amplifying 33 bp amplicons corresponding to HS1 and CS are presented. Results from two additional biological replicates are shown in Supplementary Figure S3A. (D) The HS1 protospacer (green) and the flanking plasmid DNA sequences are shown. The AAG PAM is highlighted with a red box. The TaiI recognition site is underlined. Below, primers used to amplify HS1 containing fragments of different lengths are schematically shown. (E) Results of Cas1 ChIP analysis with primer pairs amplifying HS1 amplicons of different lengths (marked as in panel D) are presented. Results from two additional biological replicates are shown in Supplementary Figure S3A. (F) Results of PCR amplification (40 cycles) of pre- and post-immunoprecipitation material from KD263 cells transformed with pG8mut plasmid. Primers complementary to HS1 and a region downstream of CRISPR array were used to amplify incorporated HS1 spacer (‘HS1’, right-hand side). Amplification of 138-bp leader fragment (‘Leader’, left hand-side) with appropriate primers was performed as a positive amplification control. (G) Results of Cas1 ChIP analysis with primer pairs amplifying 33 bp DNA fragment corresponding to HS1 in KD263 and derivative strain with deletion of the ihfA gene are presented.