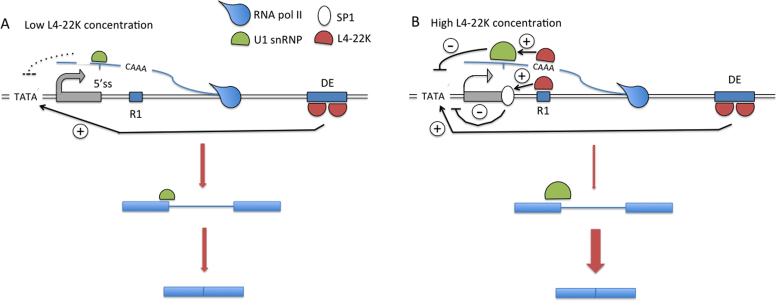
Figure 9.
A model describing a potential mechanism by which the L4-22K protein has both a positive and negative effect on MLP activity. (A) At low concentrations the L4-22K protein binds to its high affinity site, the DE element, and activates MLP transcription. (B) At high concentrations L4-22K additionally associates to its low affinity R1 binding site, both at the DNA and nascent MLTU transcript levels, which results in a reduction of MLP transcription and a concomitant enhancement of major late first intron splicing. See Discussion for further details.