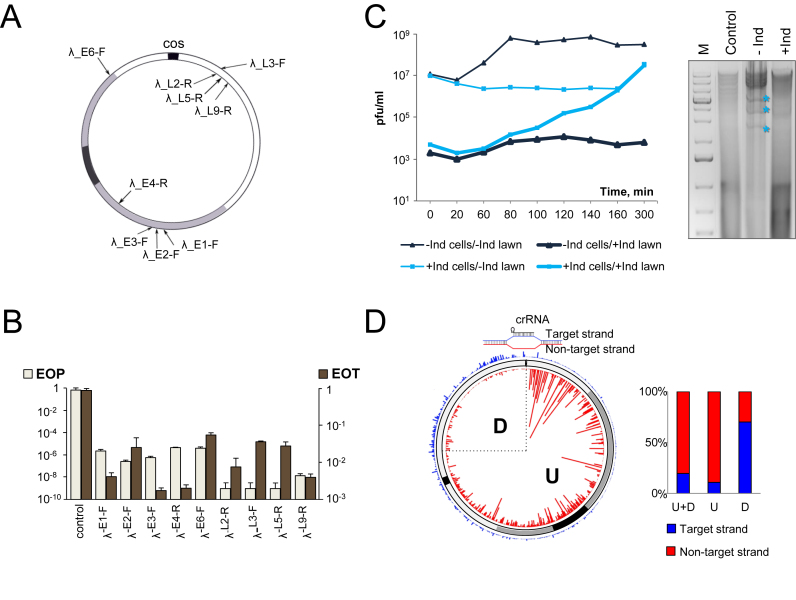
Figure 1.
The effect of CRISPR–Cas targeting on λvir infection. (A) The circular genome of bacteriophage λ formed after annealing at the cos sites is shown. The region containing immediate early genes is colored black; the region containing delayed early genes is gray, late gene region is white. Black arrows indicate the positions of protospacers targeted by crRNA spacers from different strains. Protospacers located at different strands of the genome are shown by arrows located inside and outside the circle representing the phage genome. (B) The efficiency of plaque formation (EOP) by λvir and efficiency of transformation (EOT) by cognate protospacer-containing plasmids into indicated strains. Mean values and standard deviations from three independent experiments with each strain are presented. EOP values for strains targeting additional protospacers can be found in Supplementary Table S1. (C) On the left, dynamics of plaque forming units (pfu) during the infection of induced (‘+Ind’, blue lines) or uninduced (‘–Ind’, black lines) λ-L9-R culture is shown. Phage from each infection was plated on lawns of uninduced (thin lines) and induced (thick lines) λ-L9-R cells to determine the total number of infectious phages and the number of escape phages, respectively. On the right, an agarose gel showing the products of BspHI digestion of DNA prepared from induced (‘+Ind’) and uninduced (‘–Ind’) λ-L9-R cells infected with λvir and collected 60 min post-infection is presented. ‘M’ is a molecular weight marker lane. Lane labeled ‘Control’ shows DNA from uninfected cells. Asterisks indicate restriction fragments of phage DNA. (D) Graphical representation of HTS analysis of spacers acquired during the infection of λ-L9-R cells by a λvir G-1T escape mutant. The position of the priming protospacer is indicated at the top and a structure of the R-loop formed by crRNA at this protospacer is shown. Acquired spacers are mapped on the circular viral genome. Red and blue lines show spacers matching, respectively, non-target strand and target strands. Line heights indicate relative frequency of reads corresponding to different spacers. Rectangular bars show the proportion of spacers matching the non-target (red) and target (blue) strands for the entire genome (‘U+D’); in the downstream (‘D’) quarter of the viral genome, and in the remaining upstream part (‘U’).