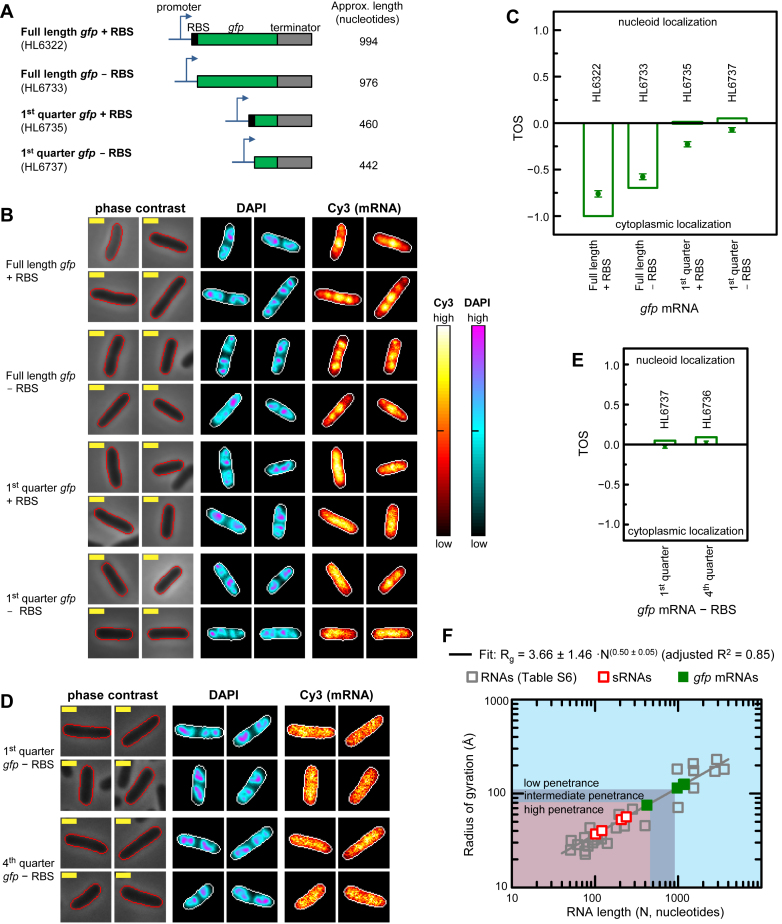
Figure 4.
RNA length and translation affect nucleoid localization. Cell edges were identified as in Figure 2A. Yellow scale bar indicates 1 μm for all images. Measurements were made at 1 mM IPTG. (A) Full and partial length gfp mRNA with and without the RBS (st7) and start codon. (B) Localization of gfp mRNA in representative cells with each of the genes in panel A. DAPI and Cy3 signal intensities (cellular normalization) represented as heat maps. Sample sizes: HL6322 (n = 113), HL6733 (n = 186), HL6735 (n = 229) and HL6737 (n = 209). (C) TOS for strains with each of the genes shown in panel A. Bars are the medians, circle symbols are the means and error bars are the SEMs. Median TOS for the following pairwise combinations were statistically significant (Mann–Whitney U two-tailed test): full length gfp mRNA ± RBS (P = 2.6 × 10−4), first quarter gfp mRNA ± RBS (P = 3.8 × 10−4) and full length gfp mRNA – RBS versus first quarter gfp mRNA – RBS (P = 1.4 × 10−27). (D) Comparison of gfp mRNA localization in cells with first quarter gfp mRNA – RBS (HL6737; n = 231) and fourth quarter gfp mRNA – RBS (HL6736; n = 205). (E) TOS for strains with the genes in panel D. Plot is presented as in panel C. The difference in median TOS was small and barely significant (P = 1.2 × 10−2, Mann–Whitney U two-tailed test). (F) Radius of gyration (Rg) as a function of RNA length. Rg values from the literature, which are provided in Supplementary Table S6, were fitted to a power function as defined in main text (gray line). Parameter values from the fit were then used to calculate Rg for the sRNA and gfp mRNAs without RBS. Two target mRNA::gfp mRNA fusions from Figure 5 are included in the plot for comparison. Because these fusions (rpoS::gfp and fhlA::gfp) have similar lengths their symbols overlap (see Figure 5 and main text for more details). Parameter errors are the standard deviations. Shading shows RNA size ranges that may have potentially high, intermediate and low nucleoid penetrance.