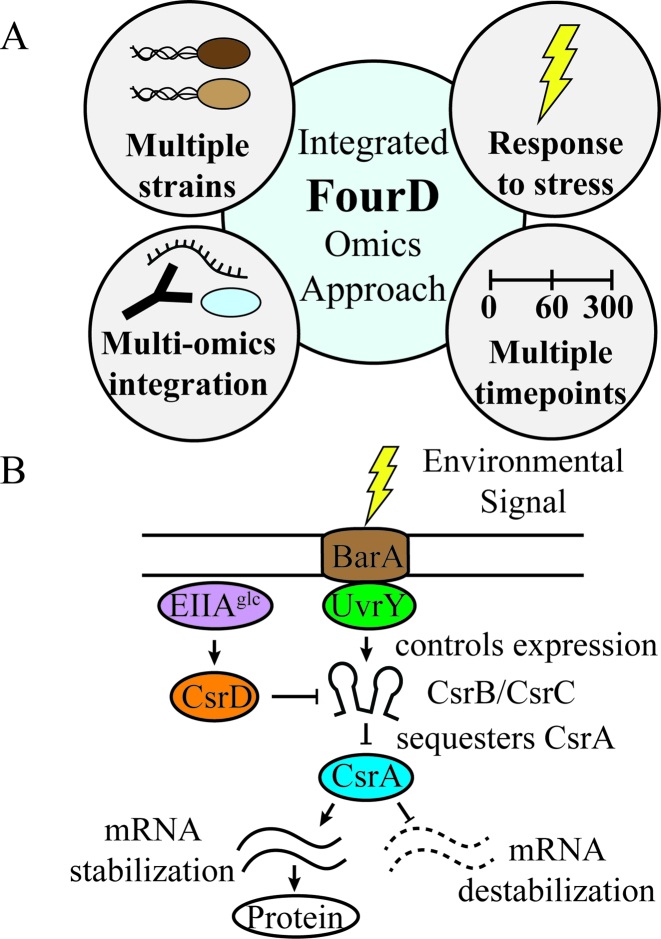
Figure 1.
Investigating the Escherichia coli carbon storage regulatory system. (A) The Integrated 4D omics (INFO) approach. This experiment focuses on integrating omics measurements to determine the targets and circuitry of a regulatory network. The four arms of the approach are using multiple mutant strains, multiple time points, multiple omics analyses and a stress to trigger the regulatory system. (B) An illustration of the basic components of the carbon storage regulatory (Csr) system. CsrA binds to a wide variety of cellular mRNAs, which affects target transcript and/or protein levels. CsrA is antagonized by CsrB and CsrC sRNAs, which bind to CsrA and prevent it from interacting with its targets. CsrD promotes degradation of CsrB and CsrC via EIIAGlc activation. The BarA and UvrY two-component system senses environmental stimuli such as formate or acetate levels and activates csrB and csrC transcription.