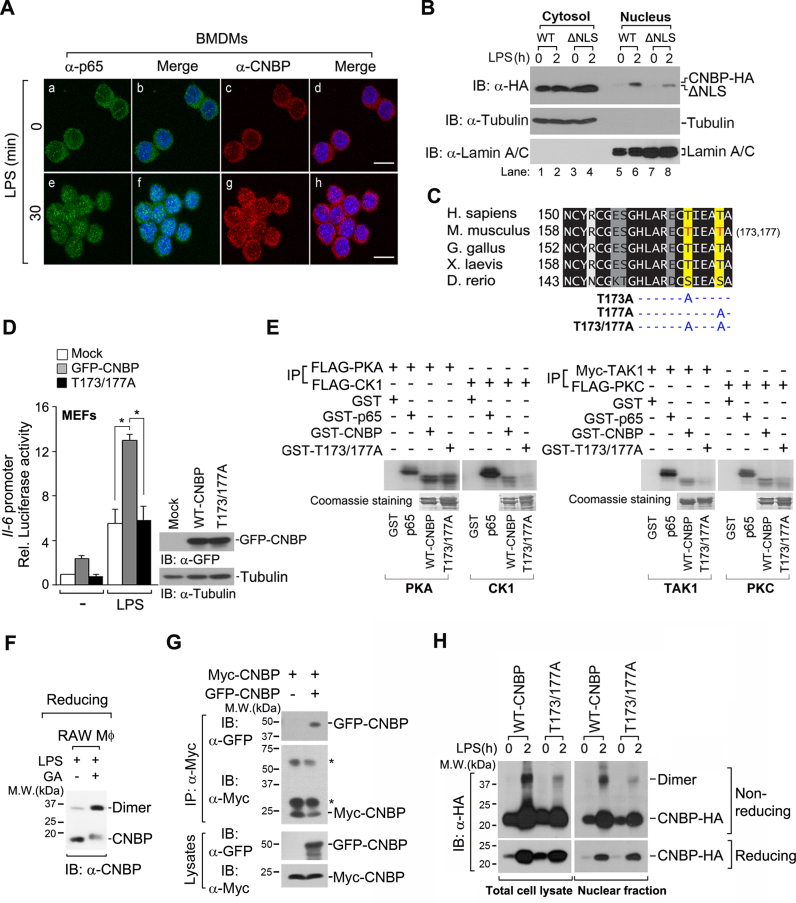
Figure 6.
LPS induces the translocation of CNBP to the nucleus by phosphorylation-mediated dimerization. (A) CNBP translocates to the nucleus from the cytosol in LPS-stimulated macrophages. Confocal microscopy of bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) that were stimulated with 80 ng ml−1 LPS for 0 or 30 min and then stained with DAPI and immunolabeled with anti-p65 antibody or anti-CNBP antibody. Scale bar, 5 μm. (B) The NLS of CNBP is important for the targeting of CNBP to the nucleus in response to LPS. Immunoblot analysis of CNBP or CNBP mutant (ΔNLS) in cytosolic and nuclear fractions of RAW macrophages after treatment with LPS (80 ng ml−1) for 0 or 2 h. Tubulin and lamin A/C were analyzed as loading controls for cytosolic and nuclear fractions, respectively. (C) C-terminal region of CNBP was aligned, and the conservation of residues is highlighted in shades of gray. Darker colors represent more conserved residues. Residues highlighted are Thr173 and Thr177 in the mouse. T173A, T177A and T173/177A indicate the point mutation at Thr173, Thr177 and Thr173/Thr177 to alanine of CNBP. (D) Both putative phosphorylation sites (Thr173 and Thr177) are required for the transcriptional activity of il-6 in response to LPS. MEFs were transfected with an empty vector (mock), wild-type GFP-CNBP vector or GFP-CNBPT173/177A vector, along with the il-6 luciferase reporter and Renilla reporter. Cells were then stimulated with LPS (80 ng ml−1) for 12 h. *P < 0.05 (Student's t-test). Immunoblot analysis of wild-type GFP-CNBP or GFP-CNBPT173/177A protein expression (right). (E) PKC, CK1 or TAK1 is responsible for LPS-mediated CNBP phosphorylation. HEK 293T cells were transfected with FLAG-PKA, FLAG-CK1, Myc-TAK1 or FLAG-PKC, and cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG or anti-Myc antibodies. Phosphorylated CNBP was resolved by sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and analyzed by autoradiography. Coomassie blue stained gels are shown in bottom panels. GST was used as a negative control. (F) Dimerization of endogenous CNBP is induced by LPS stimulation. RAW macrophages were treated with LPS (80 ng ml−1) for 2 h. GA, glutaraldehyde. (G) The formation of CNBP dimers was determined by co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP). IP of Myc-CNBP from HEK 293T cells transfected with Myc-CNBP and GFP-CNBP, followed by immunoblot analysis (IB) with antibody to Myc or GFP. Asterisks indicate the IgG heavy and light chains. (H) The phosphorylation of CNBP is critical for its dimerization. The dimer forms of the total cell lysates (left) or nuclear fraction (right) of CNBP-HA were detected by immunoblot analysis under non-reducing conditions after treatment with LPS (80 ng ml−1) for 2 h. Data are representative of three independent experiments and are presented as mean ± s.d. in D.