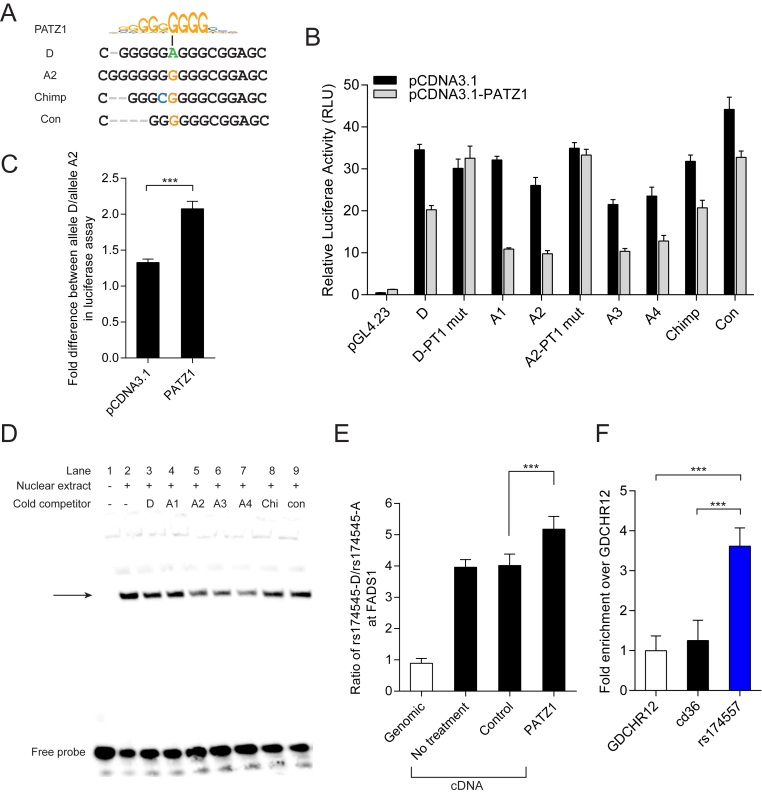
Figure 3.
PATZ1 suppresses FADS1 expression by directly binding to rs174557. (A) The D allele of rs174557 creates a less conserved PATZ1 motif compared with allele A2 (43). (B) The alleles of rs174557 were differently suppressed by PATZ1 overexpression in luciferase assay. Disrupting the predicted PATZ1 motif with both allele D (D-PT1 mut) and allele A2 (A2-PT1 mut) as templates completely abolished the suppression. Values are expressed as mean (±SD) from three independent transfections each with six technical replicates. (C) Allele A2 of rs174557 is significantly more suppressed by PATZ1 overexpression than allele D in luciferase assay. Values are expressed as fold changes of allele D versus allele A2 in luciferase activity in both control condition and under PATZ1 overexpression from B. ***P < 0.0001 with error bars represent SD. (D) The binding of biotinylated allele A2 to nuclear protein extract from HepG2 cells overexpressed with PATZ1 was differently competed by alleles of rs174557 in EMSA. The arrow indicates the shifted DNA–protein complex which was most potently competed by allele A2 (lane 5), allele A3 (lane 6) and allele A4 (lane 7). Abbreviations are as follows: Chi, chimpanzee allele; and con, the consensus sequence of AluYe5 element. (E) PATZ1 suppresses FADS1 expression in an allele specific manner with a preference for the A allele in MCF7 cells. The bars indicate allelic expression imbalance of FADS1 (mean±SD) from six replicates. ***P < 0.001 when comparing cells overexpressing PATZ1 with cells transduced with control virus. (F) ChIP-qPCR of PATZ1 chromatin binding at the rs174557 locus in HepG2 cells overexpressed with PATZ1 with antibody against FLAG epitope. The bars indicate fold changes over the negative control region GDCHR12. ***P < 0.001 calculated by two-tailed t tests. The experiments were repeated six times with error bars representing SD.