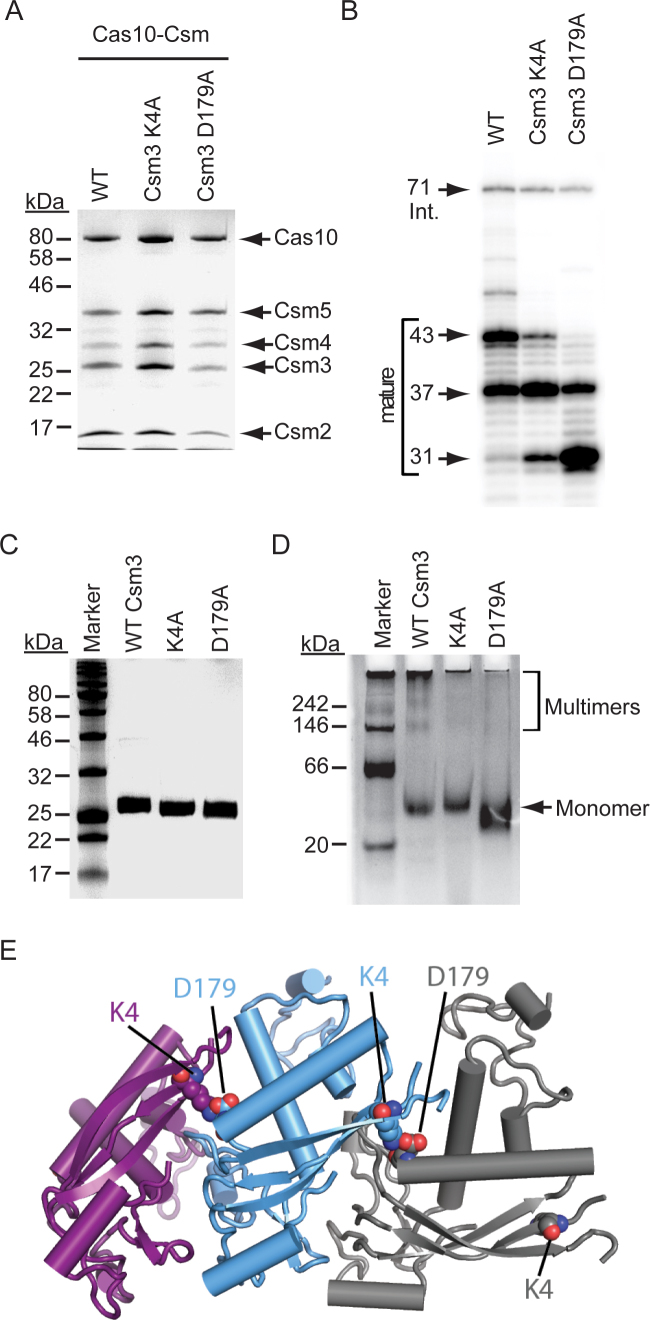
Figure 2.
Charged residues mediate Csm3 self-interactions and assemble the maturation ruler. (A) Cas10–Csm complexes containing the indicated Csm3 mutations are shown. Mutations were introduced into pcrispr-cas encoding a 6-His tag on the N-terminus of Csm2. Constructs were expressed in S. epidermidis LM1680, and whole cell lysates were subjected to Ni2+ affinity chromatography and a second purification using a biotinylated oligonucleotide antisense to spc1 crRNAs. Complexes were resolved and visualized using SDS-PAGE and Coomassie G-250 staining. Shown is a representative of at least three independent trials. (B) RNA was extracted from each complex shown in panel A, radiolabeled on the 5΄-end, and resolved using denaturing PAGE. (C) Purified recombinant Csm3 and mutant variants resolved by SDS-PAGE and visualized using Coomassie G-250 staining are shown. (D) Csm3 and mutant variants (10 pmol each) were resolved alongside the NativeMark unstained protein standard (Thermo Fisher Scientific) by blue native PAGE in which the cathode buffer contained 0.025% Coomassie G-250. Proteins were visualized using Coomassie G-250 staining. Shown is a representative of at least three independent trials. (E) Homology model of a Csm3 oligomer. The Csm3 structure was derived from the high resolution crystal structure of M. kandleri Csm3 (39), and then docked into the A. fulgidus Cmr4 backbone of a Type III-B complex (34). K4 and D179 residues are shown in space-fill.