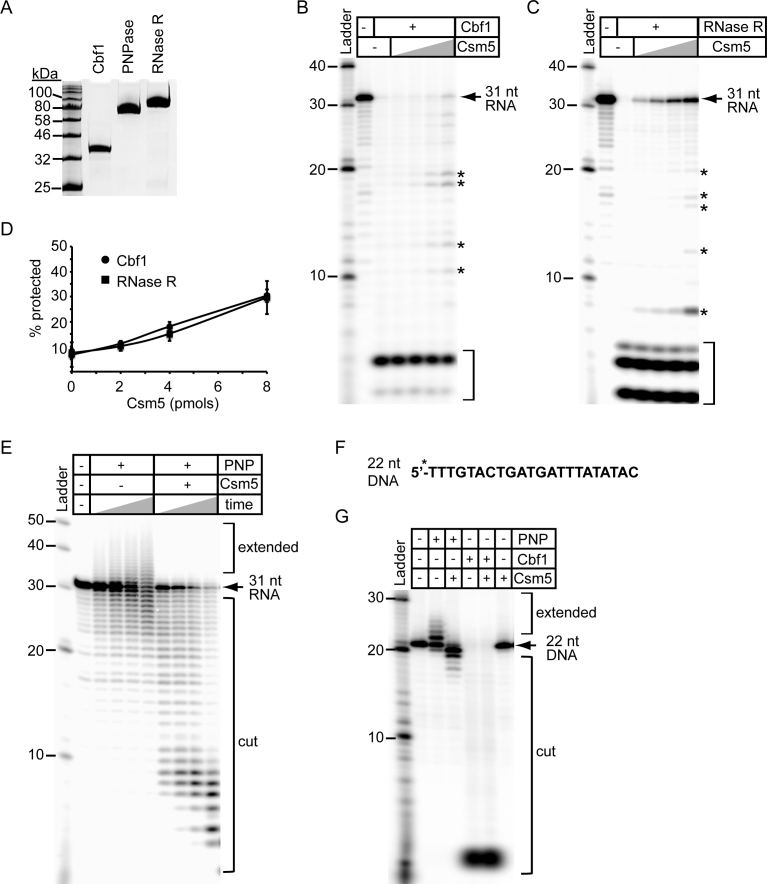
Figure 4.
Csm5 differentially modulates the activity of cellular nucleases. (A) Purified recombinant Cbf1, PNPase and RNase R resolved by SDS-PAGE and visualized using Coomassie G-250 staining are shown. (B and C) Csm5 protection against Cbf1 (B) and RNase R (C) activity is shown. 5΄-end labelled 31-nucleotide spc1 crRNA substrate (Figure 3E) was pre-incubated with increasing amounts of Csm5 (0, 1, 2, 4 and 8 pmol) before nuclease addition (1 pmol each). The reaction mixture was incubated at 37°C for 10 min. RNAs were resolved using denaturing PAGE. Full-length substrate (arrow), degradation intermediates (asterisks, *), and fully degraded substrate (brackets) are indicated. (D) Quantification of the Csm5 protection assays shown in panels B and C. Percent substrate protected was calculated as follows: ((band intensities of full length substrate + degradation intermediates)/total substrate added)) × 100. Shown is the average (±S.D.) of three independent trials. (E) PNPase (1 pmol) was combined with a radiolabeled 31 nucleotide spc1 crRNA substrate and Csm5 (4 pmols) where indicated. The reaction mixture was incubated at 37°C for increasing time points (0, 2, 5, or 10 minutes.) RNAs were resolved using denaturing PAGE. (F) The 5΄-end labelled 22-nucleotide DNA substrate used in nuclease assays. (G) PNPase or Cbf1 (1 pmol each) were combined with the DNA substrate (panel F) in the presence of Csm5 (4 pmol) where indicated. The reaction mixture was incubated at 37°C for 10 min, and DNAs were resolved using denaturing PAGE. All gel images are a representative of at least three independent trials.