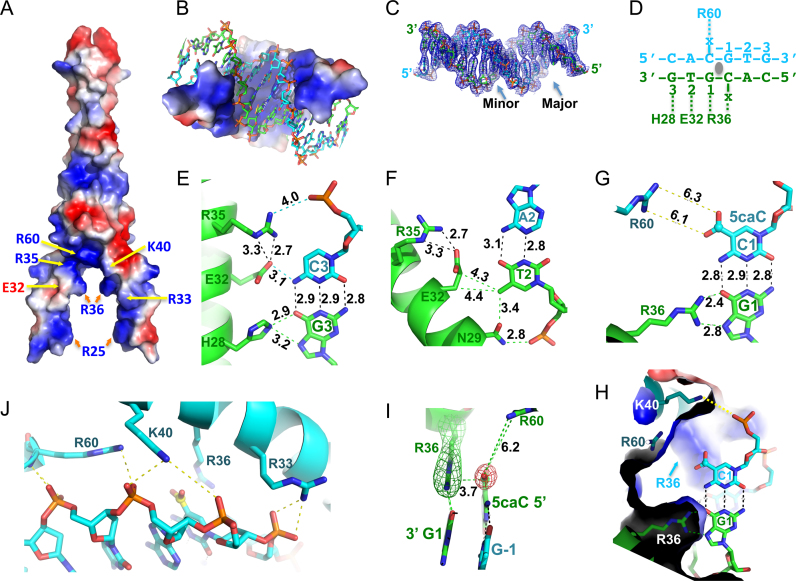
Figure 2.
Structure of MAX-5caC complex. (A) The surface charge of MAX homodimer at neutral pH is displayed as blue for positive, red for negative, and white for neutral. (B) The inner surface of the clamp-like DNA binding domain is predominantly basic. (C) Electron density 2Fo – Fc, contoured at 1σ above the mean, is shown for the entire 16-bp DNA with major and minor grooves indicated. (D) Each MAX monomer recognizes one half of the palindromic E-box sequence (x = 5caC). (E) Interactions with the outer C3:G3 base pair. The numerical numbers indicate the inter-atom distance in angstrom. (F) Interactions with the inner A2:T2 base pair. (G) The bidentate hydrogen bonds formed between Arg36 and the central G1—a pattern specific to Guanine. (H) Close-up view of the central C1:G1 base pair, recognized by the pair of Arg36 residues. Additional neighboring residues near the carboxylate group of 5caC are Lys40 and Lys60. Two 5caC:G base pairs interact with two side chains of Arg-36 residues. Lys-40 interacts with the phosphate group of 5caC. (I) Arg36 forms a 5caC–Arg–Gua triad with the central CpG dinucleotide. Simulated annealing omit electron densities, contoured at 3σ and 5σ above the mean, are shown for Arg36 (green mesh) and the carboxylate moiety of 5caC (red mesh), respectively. (J) Phosphate interactions with Arg33, Lys40 and Arg60.