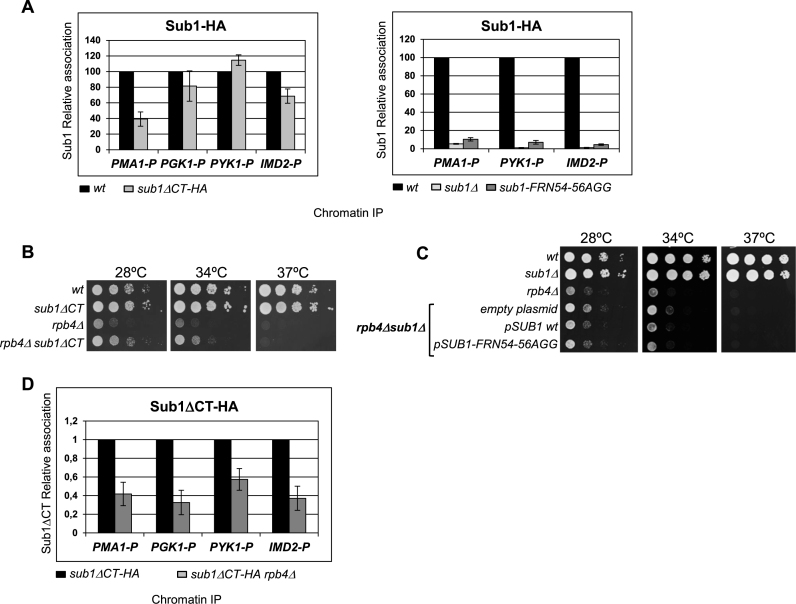
Figure 5.
Sub1 carboxy-terminal region is important for the functional interaction with Rpb4/7. (A) Left panel: Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) analyses were performed using wt and sub1ΔCT-HA strains expressing Sub1–HA. Sub1 binding to the promoter (P) of three constitutively expressed genes, PMA1, PGK1, PYK1 and the inducible gene IMD2 was examined by qPCR. Results were quantitated (as in figure 3), and relative Sub1–HA binding in sub1ΔCT-HA cells is plotted relative to that in wt cells (set equal to 100). Right panel, Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) analyses were performed using wt, SUB1 deletion mutant (sub1Δ), and the DNA binding mutant sub1-FRN54-56AGG. (B) Genetic interaction between sub1ΔCT and rpb4Δ. SUB1 deletion partially suppresses the slow growth phenotype of rpb4Δ strain at 28 and 34°C in rich medium. Serial dilutions (1:10) of wt and mutant strains were spotted on rich medium and grown for 2–3 days at the indicated temperatures. (C) There is no genetic interaction between the ssDNA binding domain of Sub1 and RPB4. Serial dilutions (1:10) of the indicated strains were spotted on selective SC medium and grown for 2–3 days at the indicated temperatures. (D) ChIP analyses were performed in wt and rpb4Δ cells expressing Sub1ΔCT-HA protein.