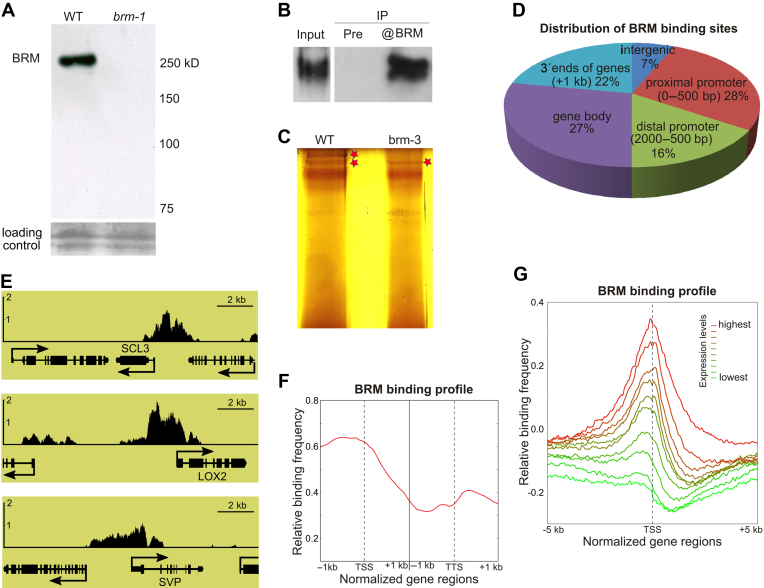
Figure 1.
Genome-wide identification of BRAHMA (BRM) occupancy using ChIP-chip. (A–C) Specificity of anti-BRM antibody used for ChIP-chip. (A) Western blot of nuclear extracts from WT and brm-1 null mutant. (B) Western blot showing precipitation of BRM from WT nuclear extracts; pre-immunization serum (Pre) was used as a negative control. (C) Silver-stained gel showing immunoprecipitated BRM (asterisks) from WT and brm-3 whole-cell extracts. (D) Distribution of BRM-bound regions throughout the Arabidopsis genome. (E) BRM occupancy at selected regions around known BRM target genes SCL3, LOX2 and SVP. Y axis represents BRM enrichment. (F) Frequency of BRM-binding sites across a virtually normalized gene unit. TSS, transcription start site; TTS, transcription termination site. (G) Analysis of average BRM binding site frequency surrounding the TSS. Genes were classified into 10 groups based on expression levels.