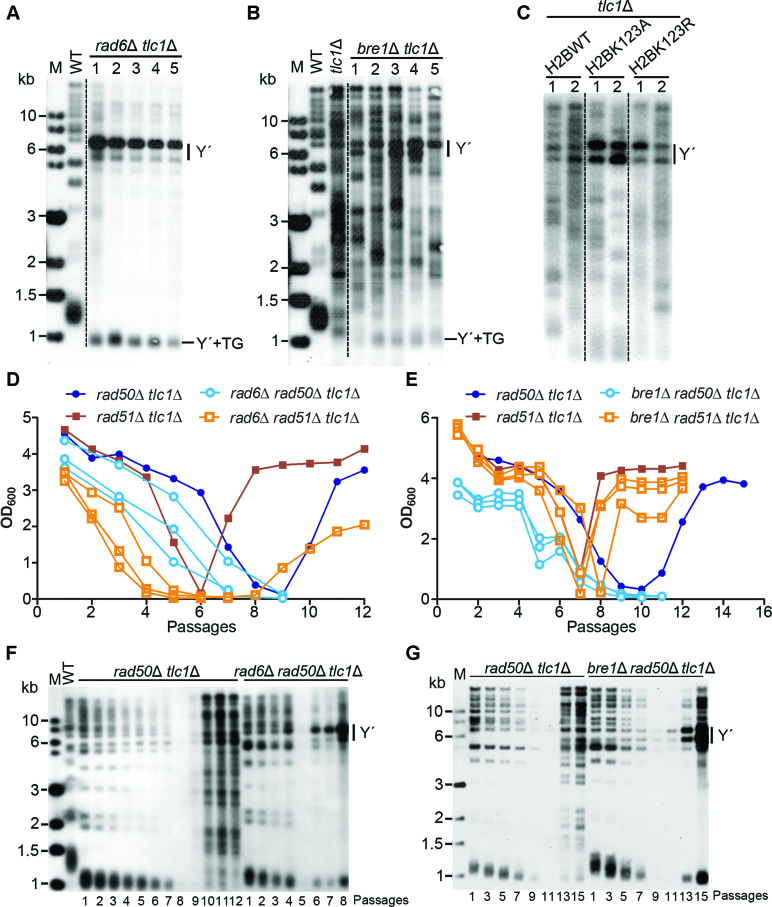
Figure 4.
Functional interaction of Rad6–Bre1 pathway and Rad50 in telomere recombination. (A–C) Southern blot analysis of telomere recombination of rad6Δ tlc1Δ, bre1Δ tlc1Δ, H2BK123A tlc1Δ and H2BK123R tlc1Δ cells cultured in liquid medium. Five clones of rad6Δ tlc1Δ (A) and bre1Δ tlc1Δ (B), and two clones of H2BK123A tlc1Δ and H2BK123R tlc1Δ (C) cells were grown in liquid cultures for about 120 generations, and genomic DNAs were extracted and digested with XhoI for Southern blot analysis. Y΄-amplification was indicated on right. (D) Cell viability assay of rad6Δ rad50Δ tlc1Δ and rad6Δ rad51Δ tlc1Δ cells in liquid cultures. TLC1/tlc1Δ RAD6/rad6Δ RAD50/rad50Δ and TLC1/tlc1Δ RAD6/rad6Δ RAD51/rad51Δ diploid strains were respectively sporulated, and tetrads were dissected. Spore colonies with indicated genotypes were subjected to cell viability assay in liquid cultures. The results of three clones of rad6Δ rad50Δ tlc1Δ and rad6Δ rad51Δ tlc1Δ were shown. (E) Cell viability assay of bre1Δ rad50Δ tlc1Δ and bre1Δ rad51Δ tlc1Δ cells in liquid cultures. The experimental procedures are the same as in D. (F and G) Southern blot analysis of telomere attrition and recombination of rad6Δ rad50Δ tlc1Δ (F), and bre1Δ rad50Δ tlc1Δ (G) cells. The strains were cultured and diluted every 48 h in liquid medium, and their genomic DNAs were extracted, digested with XhoI and subjected to Southern blot analysis.