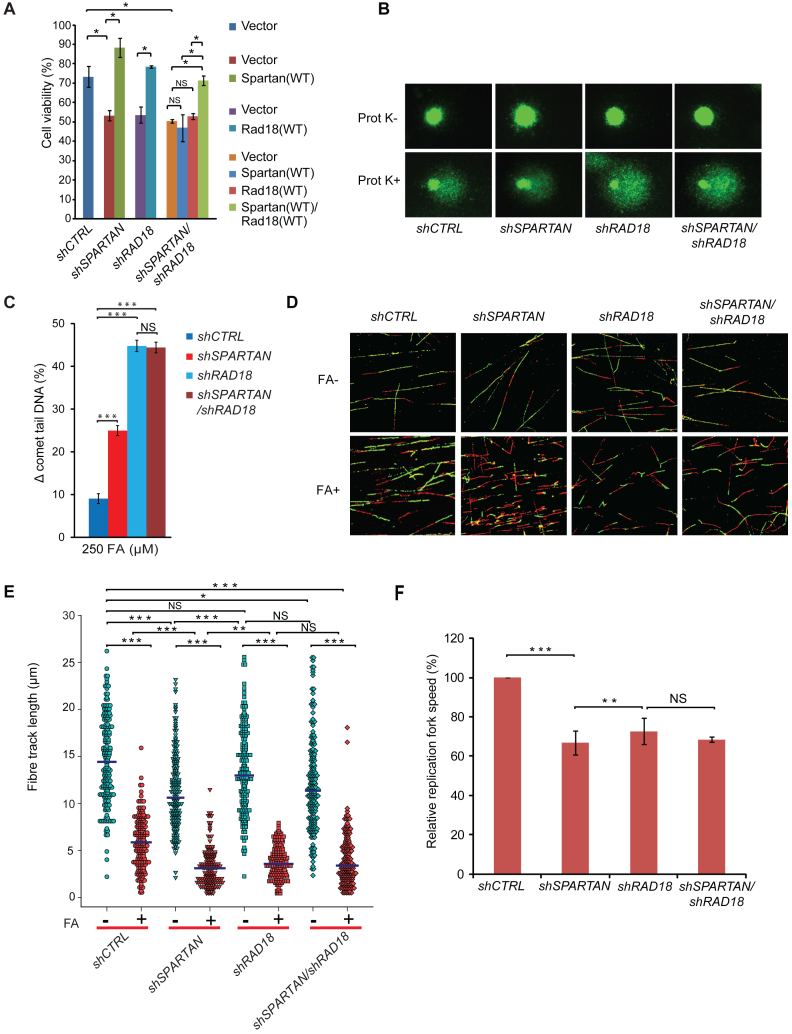
Figure 5.
Spartan and Rad18 act together in protecting genome integrity from FA-induced genotoxic stress. (A) Epistasis analysis of SPARTAN and RAD18 using cell viability assay for FA treatment. HEK 293 cells stably expressing shRNAs of SPARTAN, RAD18 and RAD18/SPARTAN or control were transfected with empty vector or N-terminally Flag-tagged SPARTAN, RAD18 or SPARTAN-RAD18 siRNA-resistant plasmid constructs. After 48 h, cells were treated with FA, and after 7 days of treatment cell viability was determined. (B) SPARTAN and RAD18 show epistatic relationship in DPC-removal. Representative images of the epistasis analysis of SPARTAN and RAD18 performed with the BrdU comet assay. The indicated cell lines were treated with 500 μM FA. (C) Quantitation of the experiment shown in (B). Statistical analysis was made by Student's t-test. Statistical significance was labelled by ***: P < 0.001, NS: not significant. (D) SPARTAN and RAD18 show epistatic relationship in the replication of DPC-containing DNA. Representative images of fibres from Spartan, Rad18 and Rad18/Spartan shRNA-silenced cells treated with FA or left untreated. (E) Quantitative measurements of second track shortening after FA treatment of different depleted cell lines, detected in the fibre assay detailed in (D), are illustrated in a dot plot diagram. Each dot represents a single measurement of the second label of a single ongoing replication fork. Three independent experiments were carried out, and at least 100 fibres per experiment per cell line were measured. Horizontal lines indicate mean values. (F) Relative replication fork speed was calculated from the quantitative measurements of the fibre assay detailed in (D) for Spartan-, Rad18- and Spartan/Rad18-depleted cells.