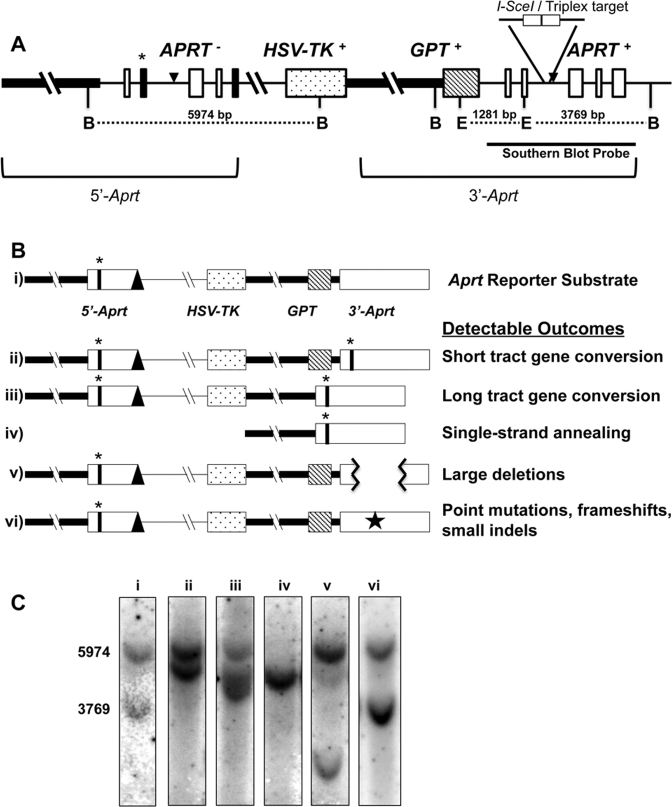
Figure 1.
Aprt intrachromosomal homologous recombination reporter substrate. (A) Schematic structure of the tandem Aprt gene-repeat reporter locus. The thick horizontal line represents the Aprt promoter region. Thin horizontal lines represent non-coding introns. Open white boxes represent non-mutated Aprt exons. Black filled boxes represent mutated exons (exon 2-point mutation and exon 5-truncation) that inactive APRT function. The dot-filled box represents the HSV-TK gene, and the diagonal-line filled box, the gpt gene. The asterisk (*) highlights the mutated EcoRV restriction endonuclease site (in exon 2). The TFO target/I-SceI sites are indicated in intron 2 of 3΄-Aprt repeat. The black triangles represent FRT sites used for locus construction. B: BglII, E: EcoRV restriction endonuclease sites. Representative repair endpoint structures are shown schematically in (B), and expected Southern blot outcomes are shown in (C) for the original substrate (i), Short tract gene conversion (STGC) (ii), Long tract gene conversion (LTGC) (iii), Single-strand annealing (SSA) (iv), an example of a Large Deletion (v), and Point mutations, frameshifts, small indels (Other) (vi) [represented by a star in panel (B)] categories when selecting against APRT function. A Southern blot representation of non-treated/non-selected cells (C-i) was included for comparison and size standards with band sizes (bp) to the left.