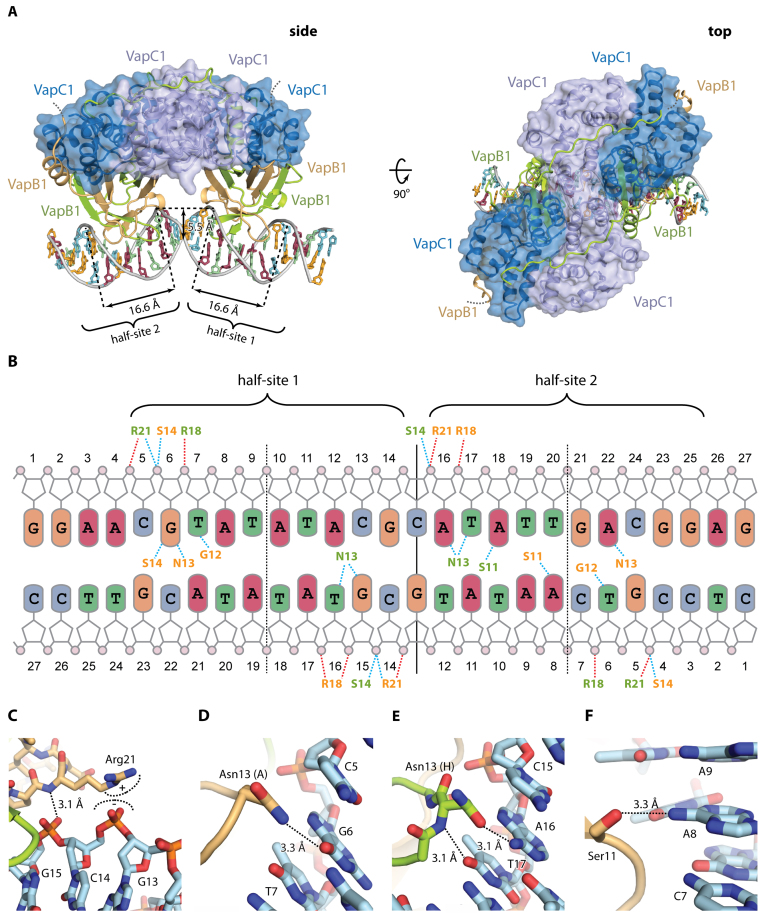
Figure 4.
Structure of VapBC1 bound to operator DNA. (A) Two orthogonal views of the VapBC1 heterooctamer (blue/green/light brown) bound to DNA with the VapC homotetramer in a semi-transparent surface representation, and DNA bases coloured as in B. In the side view (left), the positions of half-sites 1 and 2 are indicated with the widths of the major grooves and depth of the minor groove shown. The disordered VapB C termini are shown with dashed lines. (B) Schematic overview of the interactions between VapBC1 and DNA. Dashed lines indicate hydrogen bonds (blue) and electrostatic interactions (red) to phosphate groups (pink circles) and bases (coloured rounded squares). Residues in VapB1 are shown in colours matching panel A (light brown/green). Vertical lines indicate the operator pseudo 2-fold axis separating the two half sites (solid) as well as the half site 2-fold axes (dashed), and the extent of the two half-sites are indicated as well. (C) Interactions of VapB1 Arg21 with DNA. (D) Interactions of VapB1 Asn13 (chain A) with DNA. (E) Interactions of VapB1 Asn13 (chain H) with DNA, showing that it flips the side chain to reverse the hydrogen bond polarity in the other molecule. (F) Interactions of VapB1 Ser11 with DNA. Ser11 forms a base-specific hydrogen bond with A8 in half-site 2.