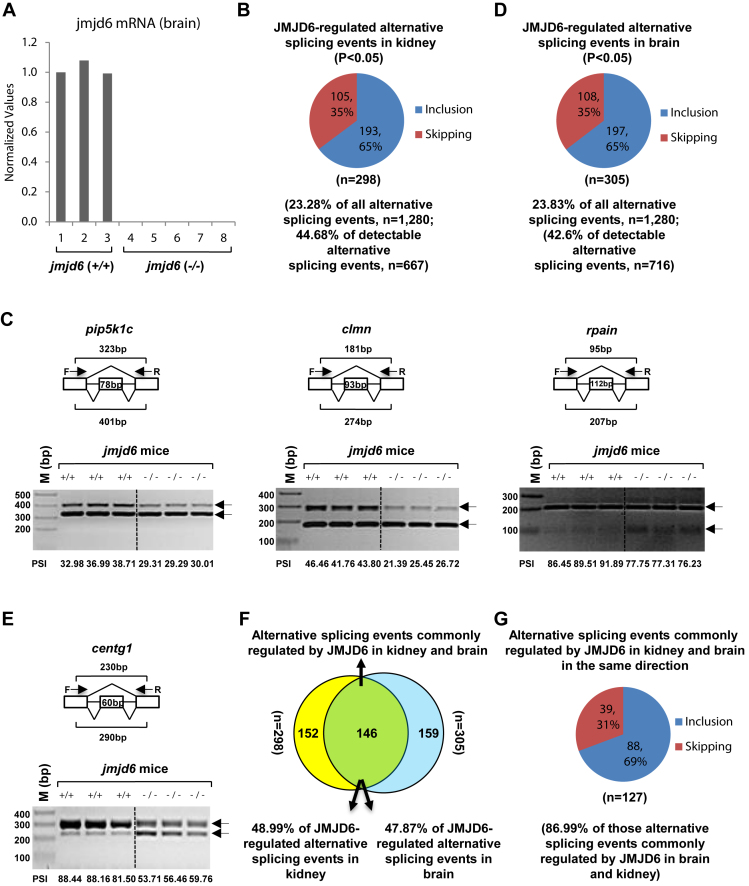
Figure 3.
JMJD6 regulates alternative splicing in vivo. (A) RNAs were extracted from kidney and brain samples of wild type (jmjd6 (+/+)) (n = 3) or jmjd6 knockout (jmjd6 (−/−)) (n = 5) mice, and the expression of jmjd6 was examined through RT-qPCR. Data shown was jmjd6 expression in brain samples. (B,D) Pie chart showing alternative splicing events, both exon inclusion and skipping, regulated by jmjd6 in kidney (B) or brain (D) samples examined through RASL-Seq analysis using RNA samples described in (A) (P < 0.05). (C, E) RT-PCR was done using RNA samples from kidney (C) or brain (E), both wild type (+/+, n = 3) and jmjd6 knockout (−/−, n = 3), as described in Figure 3A to validate alternative splicing events (exon inclusion) regulated by JMJD6 detected by RASL-Seq. Representative examples were shown as follows: pip5k1c (NM_008844, exon 17) (Figure 3C, left panel); clmn (NM_053155, exon 13) (Figure 3C, middle panel); rpain (NM_027186, exon 4) (Figure 3C, right panel); centg1 (NM_001033263, exon 14) (E). F: forward primer; R: reverse primer; bp: base pair. (F) Venn diagram showing overlapping between JMJD6-regulated alternative splicing events in kidney and brain (P = 0.002229, hypergeometric test, expected background value: 24). (G) Pie chart showing alternative splicing events commonly regulated by JMJD6 in kidney and brain in the same direction, including exon inclusion and skipping (P < 0.05).