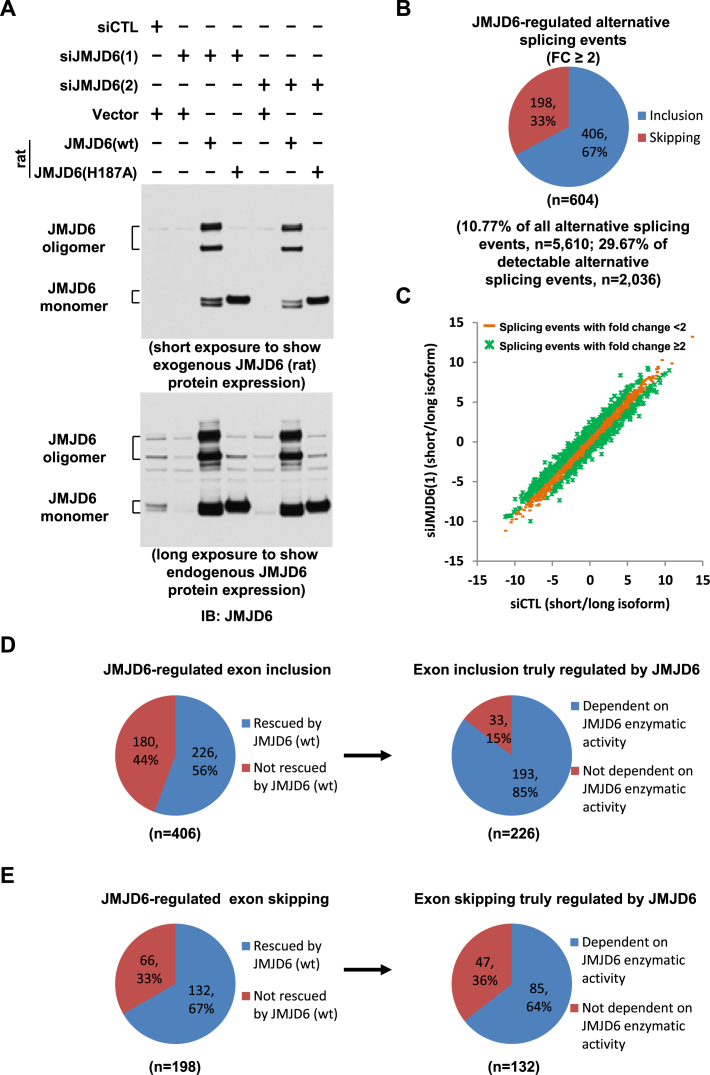
Figure 6.
JMJD6 enzymatic activity is involved in its regulated alternative splicing. (A) HEK293T cells were transfected with control siRNA (siCTL) or two independent siRNAs specifically targeting JMJD6 (siJMJD6(1), siJMJD6(2)) in the presence or absence of a control vector or vectors expressing rat wild-type JMJD6 (wt) or its enzymatically deficient mutant with substitution of histidine 187 to alanine (H187A), followed by immunoblotting (IB) with anti-JMJD6 antibody. JMJD6 monomer and oligomer were shown as indicated. (B) Pie chart showing alternative splicing events regulated by JMJD6, both exon inclusion and skipping (FC≥2), examined through RASL-Seq analysis (expanded version) using RNA samples described in (A). Data shown was from siJMJD6(1). (C) Scatter plot showing the isoform ratio (short versus long, log2) of all detectable alternative splicing events in RASL-Seq (expanded version) when knocking down JMJD6. (D, E) Left panels: Pie chart showing exon inclusion (D) or skipping (E) regulated by JMJD6, including the ones could be rescued by JMJD6 protein (referred as exon inclusion (D) or skipping (E) truly regulated by JMJD6) and the ones could not; Right panels: Pie chart showing exon inclusion (D) or skipping (E) truly regulated by JMJD6 including the ones were dependent on JMJD6 enzymatic activity and the ones were not.