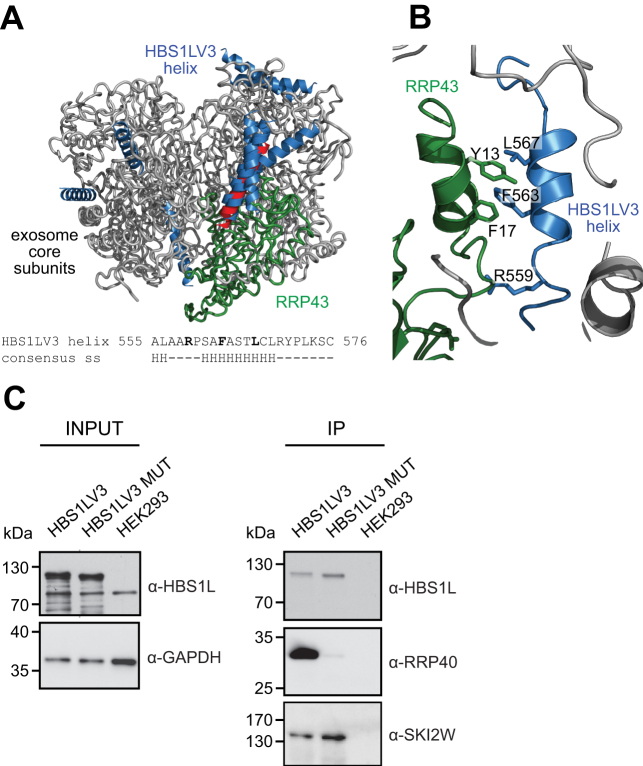
Figure 6.
Model of HBS1LV3-exosome interactions. HBS1LV3 helix (aa 555–576) docks into the surface of RRP43. (A) Modeled human HBS1LV3 helices docked into the exosome core (PDB code: 2NN6, (39)) are shown in blue. The RRP43 protein is shown in green. The remainder of the human exosome complex is colored grey. The 10 best predictions are shown, with 5 predictions docking into the same position on the surface of the RRP43 exosome subunit. The highest ranking prediction is colored red. Bottom: secondary structure prediction of HBS1LV3 fragment. (B) A magnified view of interactions. (C) R559, F563 and L567 HBS1LV3 amino acids are crucial for interactions with the exosome complex. Total cell extracts were prepared from HEK293 cells transiently transfected with vectors expressing either EGFP-tagged HBS1LV3 (WT) or HBS1LV3 MUT (R559A, F563A, L567A) proteins. Co-IPs were performed using GFP trap resin. The complete cell extracts (INPUT) and precipitated proteins (IP) were separated by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by Western blotting. α-HBS1L, α-RRP40 and α-SKI2W antibodies were used to visualize precipitated proteins. α-GAPDH antibodies were utilized as a loading control.