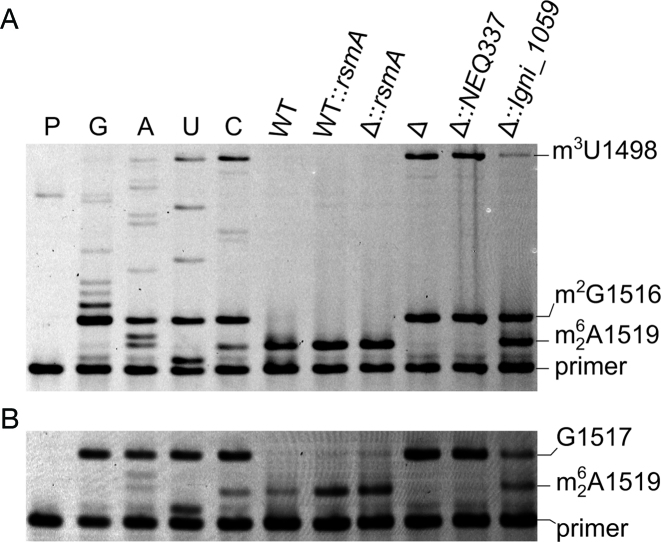
Figure 2.
Primer extension on rRNAs from Escherichia coli strains. (A) The dideoxy sequencing reactions (C, U, A and G) were carried out on rRNA from the rsmA null-mutant (Δ). Extension reactions were on rRNA from the wild-type (WT) strain; the wild-type strain with an extra, plasmid-encoded copy of the E. coli rsmA gene (WT::rsmA); the rsmA null-mutant with plasmid-encoded rsmA (Δ::rsmA); the uncomplemented rsmA null-mutant (Δ); the rsmA null-mutant with plasmid-encoded NEQ337 (Δ::NEQ337); and the rsmA null-mutant with plasmid-encoded Igni_1059 (Δ::Igni_1059). Adenosine dimethylation at A1518/1519 halts reverse transcription; the m2G1516 modification is in all the E. coli strains and causes pausing; the m3U1498 modification (also present in all strains) causes a complete stop. P, primer only. (B) Primer extension on the same rRNA samples replacing dCTP with ddCTP in all reactions to obtain a complete stop at G1517 against which the bands for dimethylated A1518 and A1519 were quantified. Under the growth conditions used here, Igni_1059 dimethylated approximately 50% of the E. coli nucleotides A1519 and/or A1518. These nucleotides were dimethylated to >95% by E. coli's own RsmA enzyme (WT), and no further increase in modification was achieved by over-expressing an extra copy of the rsmA gene (WT::rsmA).